Publications
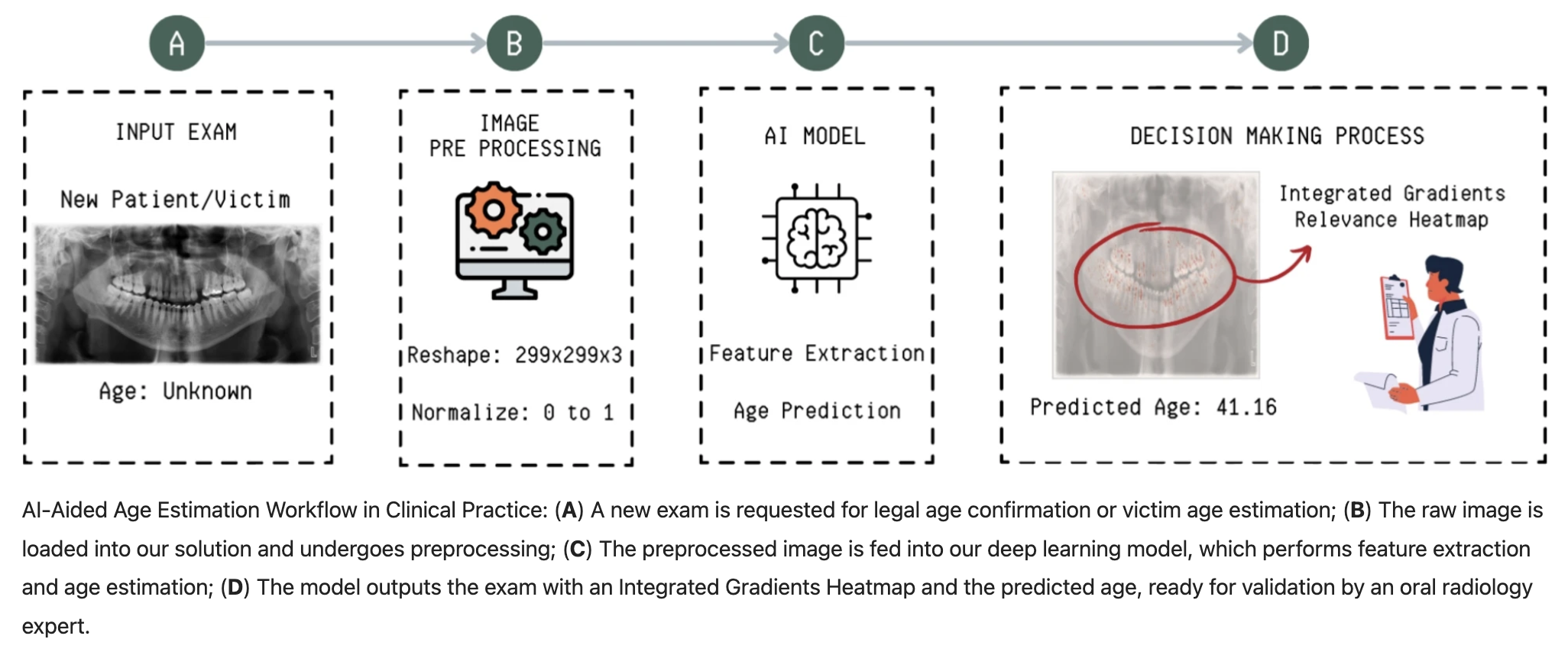
We use Deep Learning to forecast the Ibovespa, striving to balance high forecasting accuracy with model interpretability, to improve decision-making in time-series forecasting and provide valuable insights into the economic landscape of Brazil…
W. OLIVEIRA; M. A. SANTOS; C. A. A. P. BURGARDT; M. L. A. PONTUAL; C. ZANCHETTIN
Nature Scientific Reports, 2024
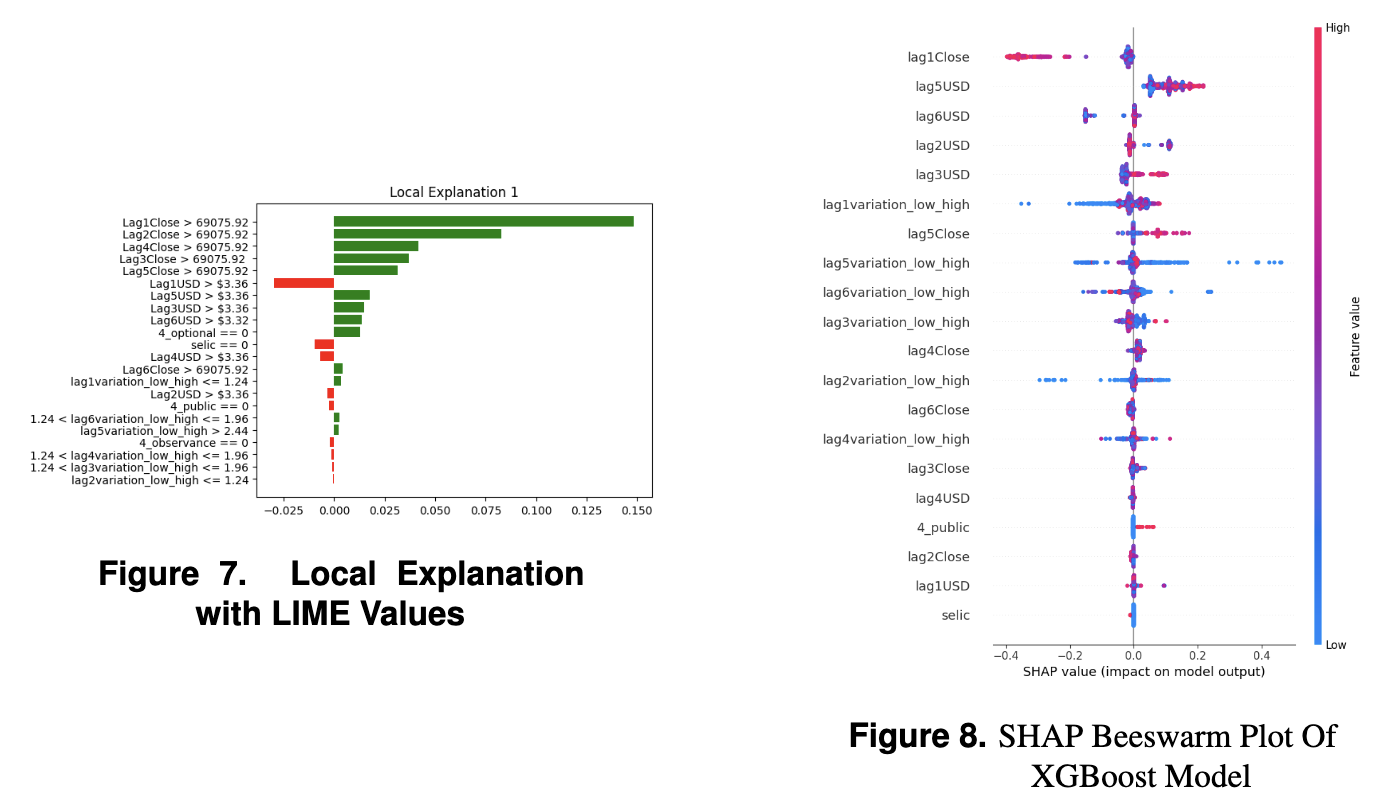
We use Deep Learning to forecast the Ibovespa, striving to balance high forecasting accuracy with model interpretability, to improve decision-making in time-series forecasting and provide valuable insights into the economic landscape of Brazil…
L. R. A. MORAIS; G. A. M. FRAGOSO; T. B. LUDERMIR; C. L. A. MONTEIRO
Encontro Nacional de Inteligência Artificial e Computacional (ENIAC), 2024
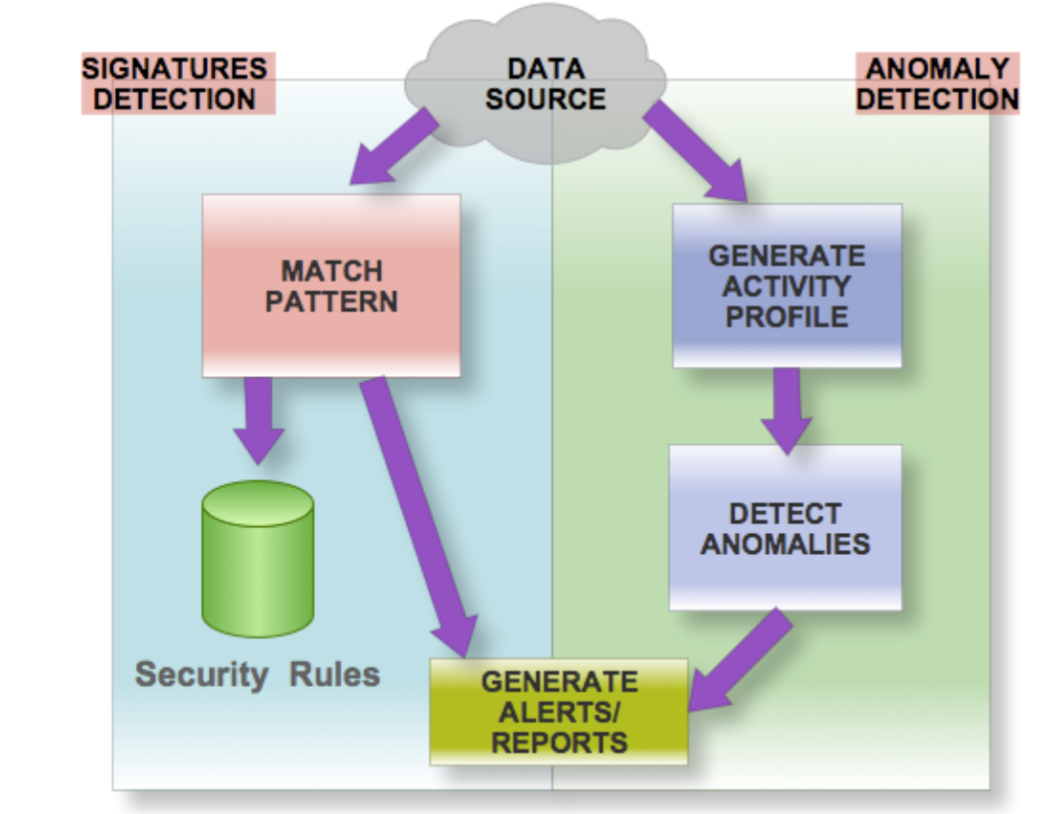
We perform a comparative analysis between 3 state-of-the-art key information extraction models. We assess the performance of LAMBERT, LayoutLM, and LayoutLMv2 models considering different metrics..
A. ALMEIDA; L. GONÇALVES; C. ZANCHETTIN; B. L. D. BEZERRA
IEEE Latin American Conference on Computational Intelligence (LA-CCI), 2023
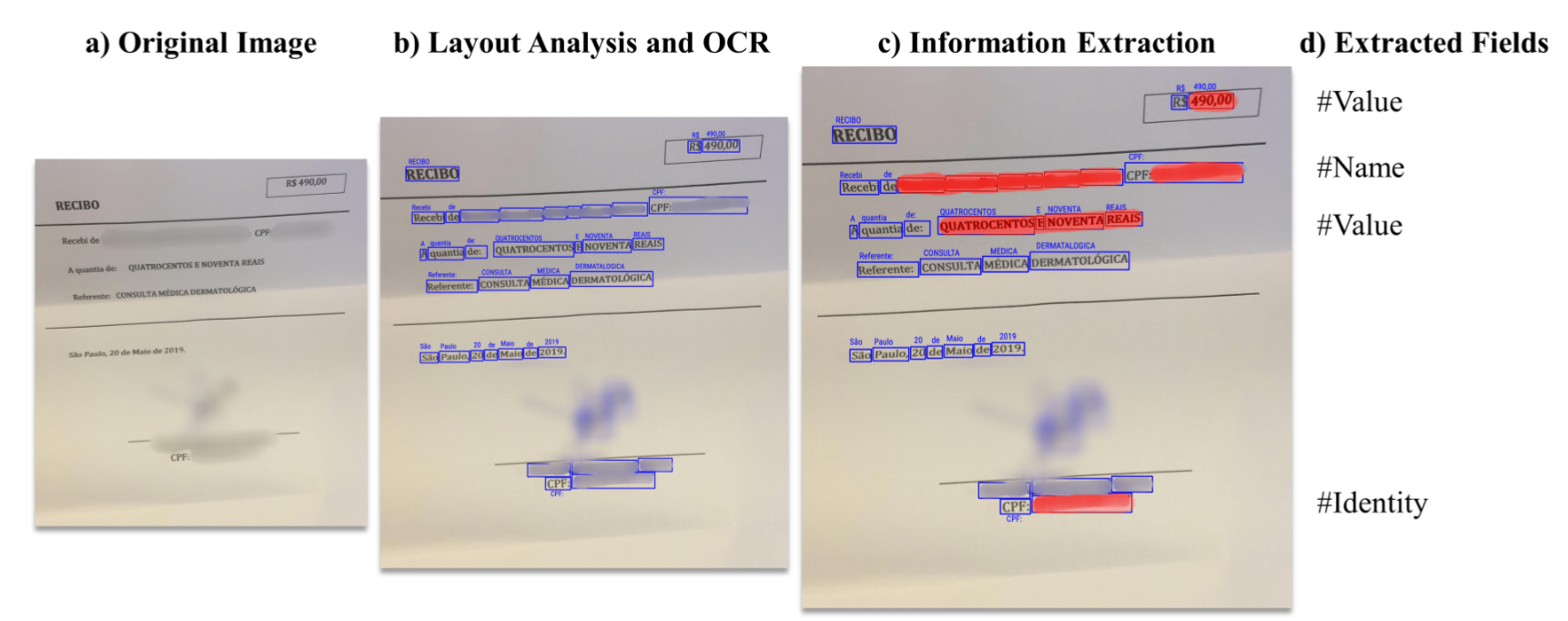
We perform a comparative analysis between 3 state-of-the-art key information extraction models. We assess the performance of LAMBERT, LayoutLM, and LayoutLMv2 models considering different metrics..
J. MACEDO, B. BEZERRA, E. LIMA, A. SOARES, C. LOPES AND C. ZANCHETTIN
IEEE Latin American Conference on Computational Intelligence (LA-CCI), 2023
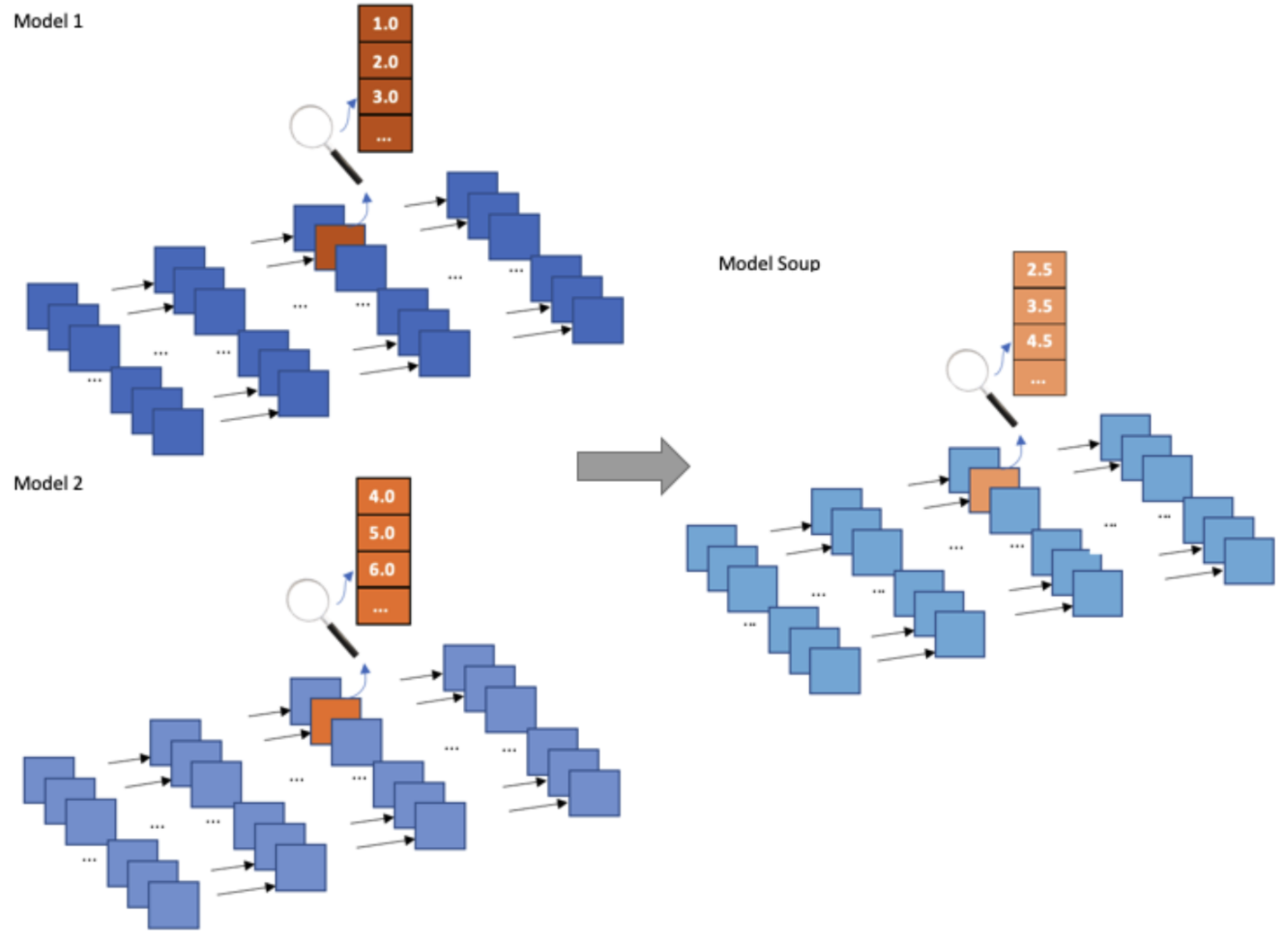
We evaluates the state-of-the-art NER models BiLSTM+CRF and BERT+Fine-Tunning trained on Portuguese corpora through finetuning in the legal and legislative domains.
M. L. B. MONTEIRO, C. ZANCHETTIN
Brazilian Conference on Intelligent Systems, 2023
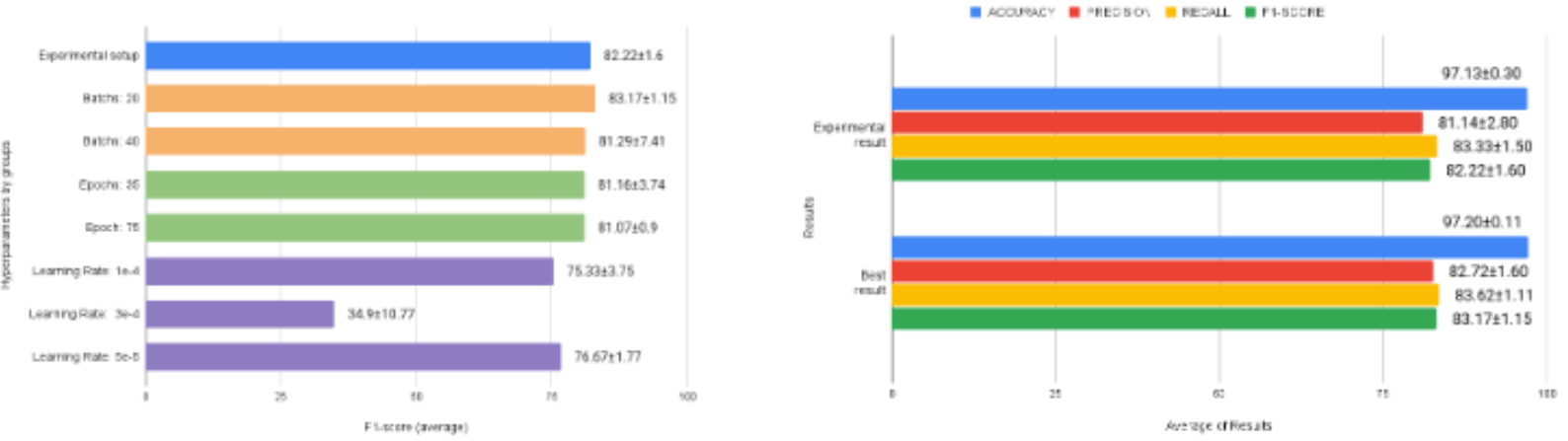
We evaluates the state-of-the-art NER models BiLSTM+CRF and BERT+Fine-Tunning trained on Portuguese corpora through finetuning in the legal and legislative domains.
H. O. ALBUQUERQUE, E. SOUZA, A. L. I OLIVEIRA, D. L. MACEDO, D. VITORIO, C. ZANCHETTIN, N. F. F. SILVA, A. C. P. L. F CARVALHO
Portuguese Conference on Artificial Intelligence, 2023
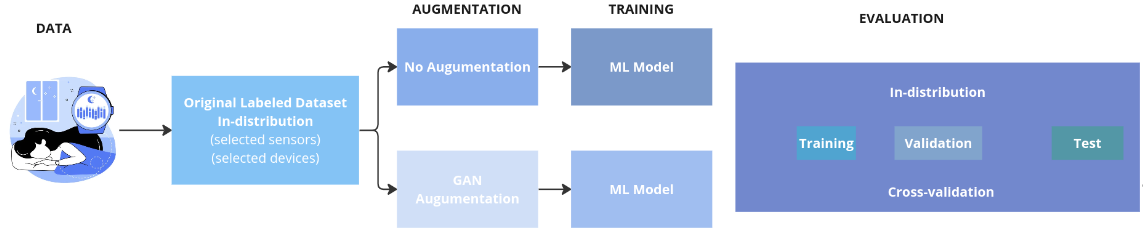
We analyze the performance of three Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) and a Diffuse model, considering fidelity, diversity, and generalization metrics. In addition, we assess the relationship between the addition of synthetic samples to the training data and the impact of imbalanced classes on the generative model in the production of synthetic samples. We also introduce a novel GAN designed to generate synthetic samples of time series data from wearable devices.
M. D. SOUZA, C. R. SILVA JUNIOR, A. L. SANTOS, J. QUINTINO, F. Q. B. SILVA, C. ZANCHETTIN
INNS Deep Learning Innovations and Applications, 2023
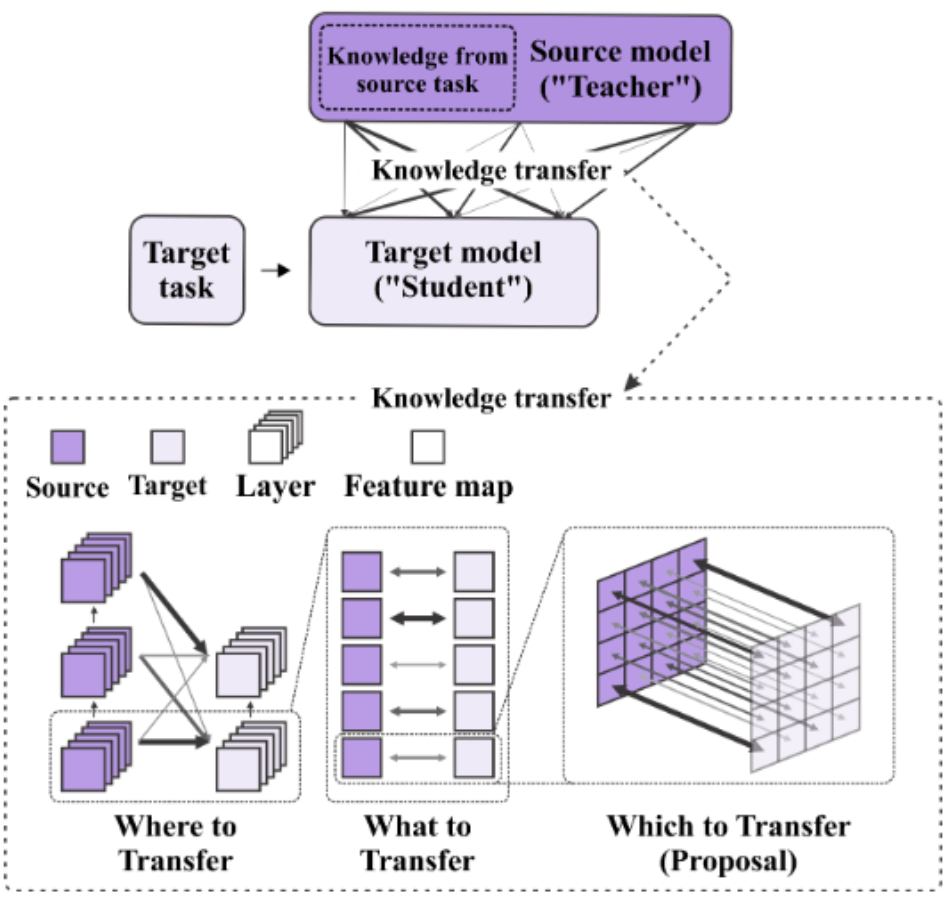
We propose add pixel-level information in addition to layers and channels information from the source network to guide the target network training. The idea is to use meta-networks to enhance the knowledge transfer process bridging the source and target networks, deciding which pairs of information should be matched for optimal knowledge transfer.
L. L. NOGUEIRA, F. M. DE PAULA NETO, D. L. MACEDO, A. L. I. OLIVEIRA, C. ZANCHETTIN
International Joint Conference on Neural Networks, 2023
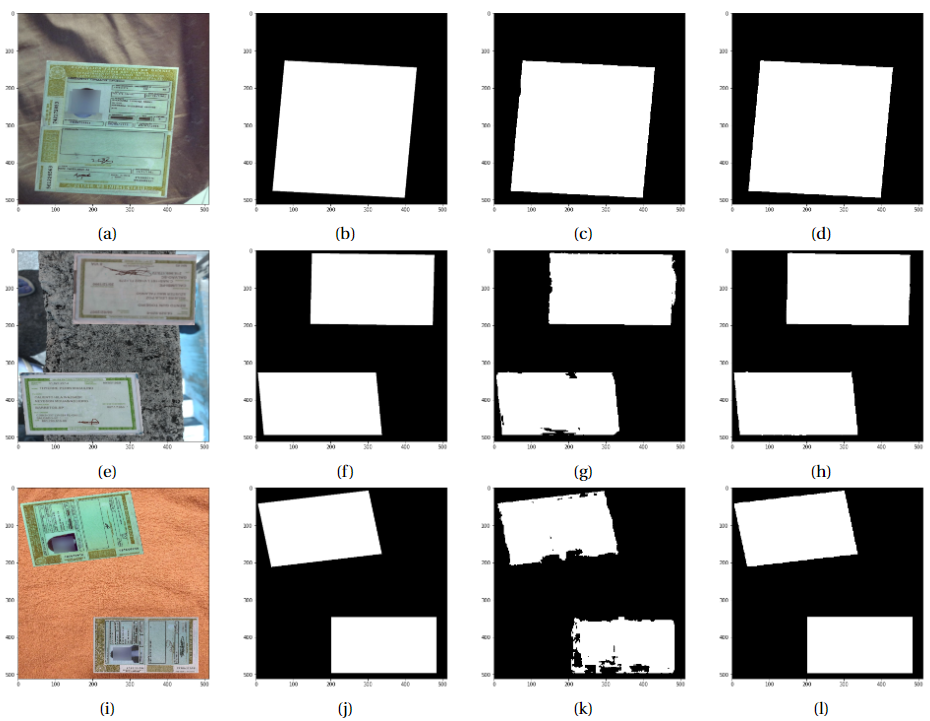
We propose a new fully convolutional network architecture based on U-Net for segmentation associated with self-calibrated convolution.
I. R. RODRIGUES, L. G. F., SILVA, D. L. MACEDO, C. ZANCHETTIN, P. T. ENDO, D. SADOK
International Joint Conference on Neural Networks, 2023
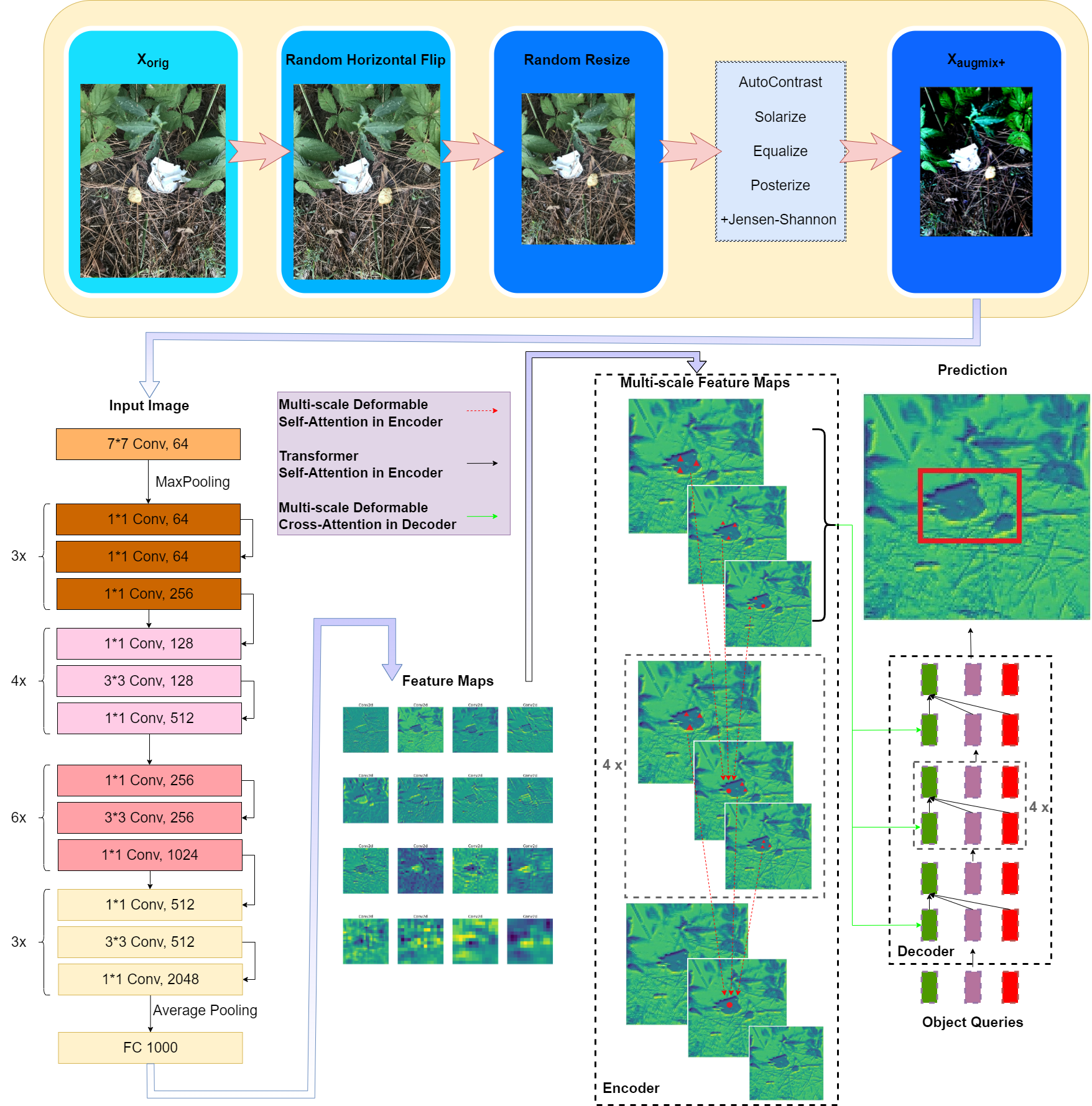
We present a novel method for enhancing the robustness of image detection models using AUGMIX. Our approach involves applying various augmentations to the input images in a stochastic manner, resulting in a single output image after all transformations have been applied.
E. CUNHA, D. L. MACEDO, C. ZANCHETTIN
International Joint Conference on Neural Networks, 2023
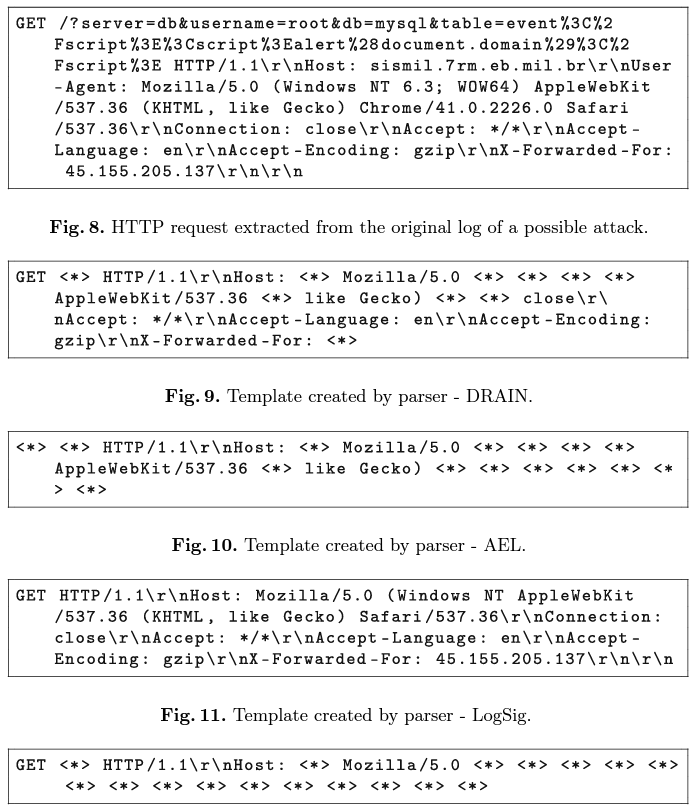
We present the RequestBERT-BiLSTM, a new model to detect possible HTTP request attacks without using Log Parser.
RAMOS JUNIOR, L. S., D. L. MACEDO, A. L. I. OLIVEIRA, C. ZANCHETTIN
Brazilian Conference on Intelligent Systems, 2022
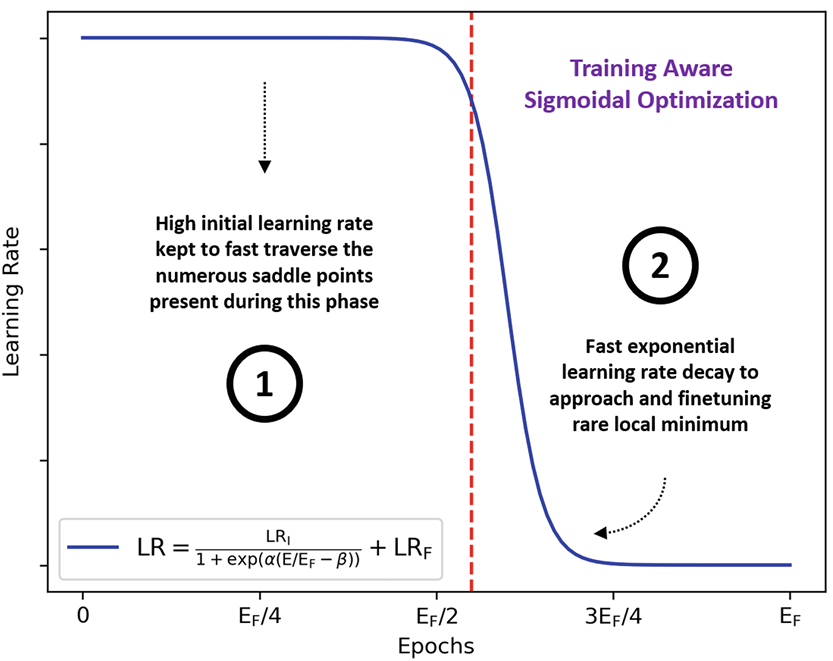
We proposed the Training Aware Sigmoidal Optimizer (TASO), consisting of a two-phase automated learning rate schedule. The first phase uses a high learning rate to fast traverse the numerous saddle point, while the second phase uses a low learning rate to approach the center of the local minimum previously found slowly.
D. L. MACEDO, P. H. D. LEUCHTENBERG, T. B. LUDERMIR, C. ZANCHETTIN
Brazilian Conference on Intelligent Systems, 2022
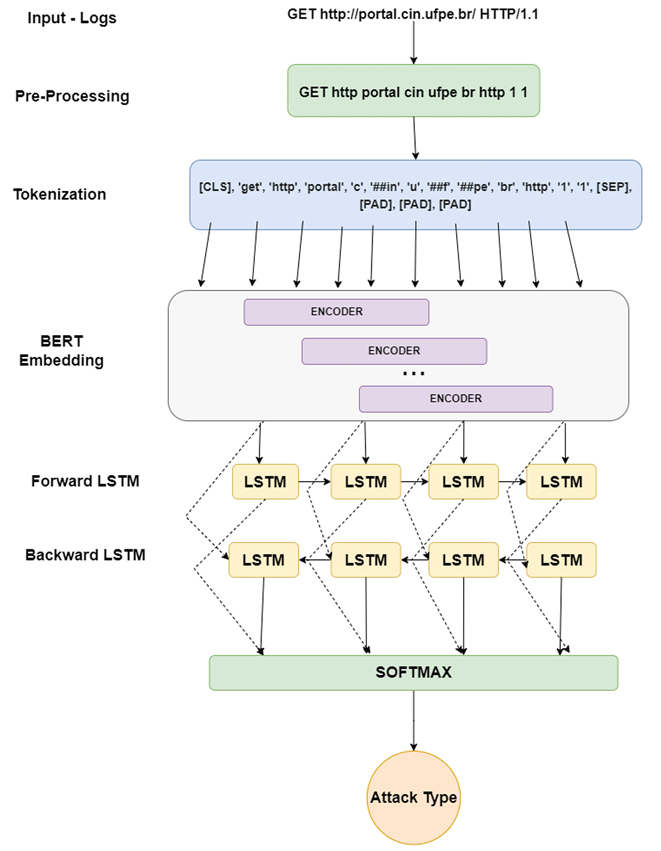
We propose a new approach to detect possible attacks on HTTP requests based on machine learning. The new model LogBERT-BiLSTM uses BERT and Bidirectional LSTMs to detect anomalies in data.
RAMOS JUNIOR, L. S., MACEDO, A. L. I. OLIVEIRA, C. ZANCHETTIN
International Conference on Artificial Neural Networks, 2022
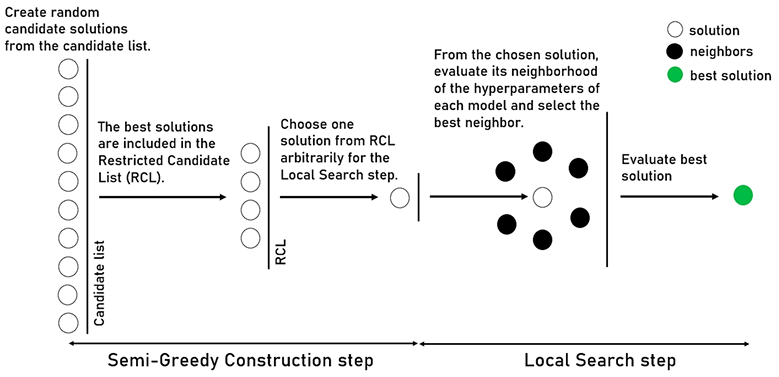
We propose a simple and effective approach based on the Greedy Randomized Adaptive Search Procedure (GRASP) algorithm that we adapt to optimize deep neural networks models.
A. A. SILVA, A. S. XAVIER, D. L. MACEDO, A. L. I. OLIVEIRA, C. ZANCHETTIN
International Joint Conference on Neural Networks, 2022
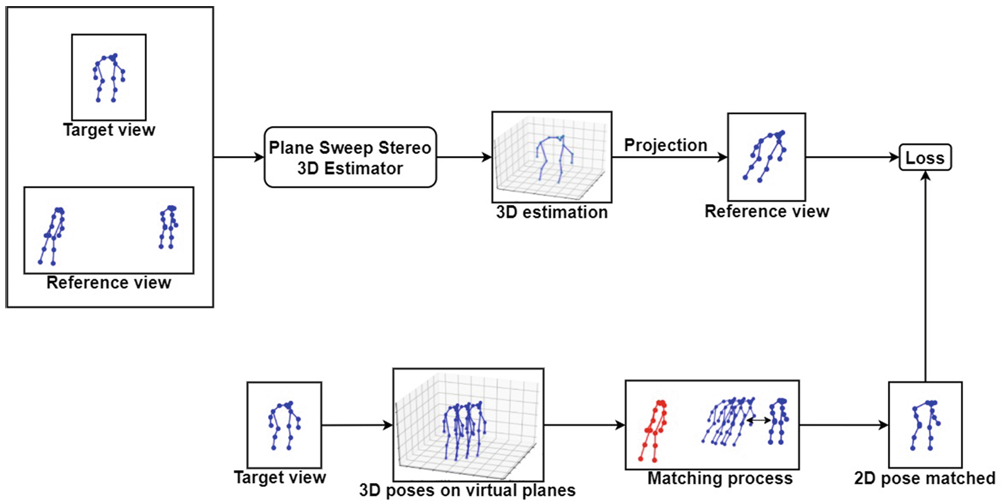
We propose an unsupervised approach to estimating 3D human poses requiring only an off-the-shelf 2D pose estimation method and the intrinsic and extrinsic camera parameters.
D. W. F. SILVA; J. P. S. M. LIMA, D. L., MACEDO, C. ZANCHETTIN; D. G. F., THOMAS; H. UCHIYAMA; V. TEICHRIEB
International Conference on Artificial Neural Networks, 2022
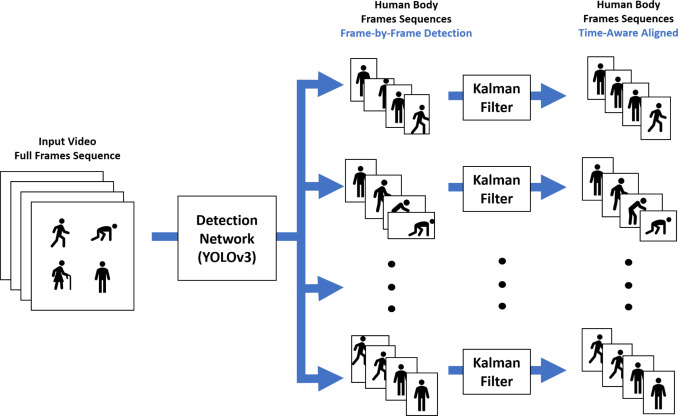
We propose two options for the overall end-to-end trainable architectures. The first option is created using the YOLOK tracking stage with a classification stage based on the 3DCNN classification block. The second option is created by combining the YOLOK tracking stage with a classification stage.
M. E. N. Gomes, D. Macêdo, C. Zanchettin, P. S. G. Mattos-Neto and A. L. I. Oliveira
Computer Vision and Image Understanding, 2022
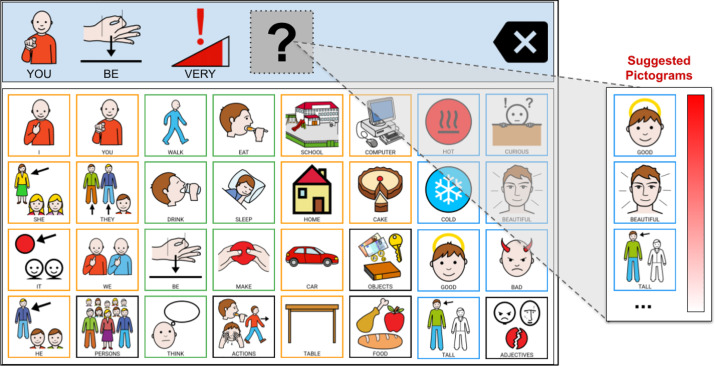
We present PictoBERT, an adaptation of BERT for the next pictogram prediction task. We changed the BERT’s input embeddings to allow word-sense usage instead of words, considering that a word-sense represents a pictogram better than a simple word.
J. A. Pereiraa, D. Macêdo, C. Zanchettin, A. L. I. Oliveira and R. N. Fidalgo
Expert Systems with Applications, 2022
We propose the KutralNext architecture, an efficient model for single- and multi-label fire and smoke recognition tasks.
A. Ayala, B. Fernandes, F. Cruz, D. Macêdo and C. Zanchettin
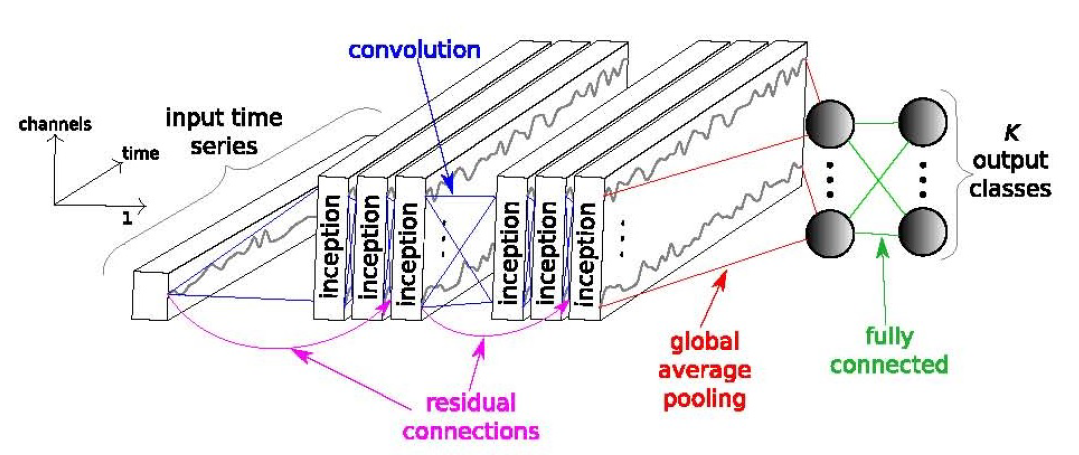
We propose signature identification of these colony odors from microorganisms using InceptionTime. The InceptionTime model is a set of models of the deep convolutional neural network, inspired by the Inception-v4 architecture.
P. J. M. Vasconcelos, D. Macêdo, L. M. Almeida, R. L. G. Neto, C. A. Benevides, C. Zanchettin, A. L. I. Oliveira
IEEE International Conference on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics (SMC), 2021
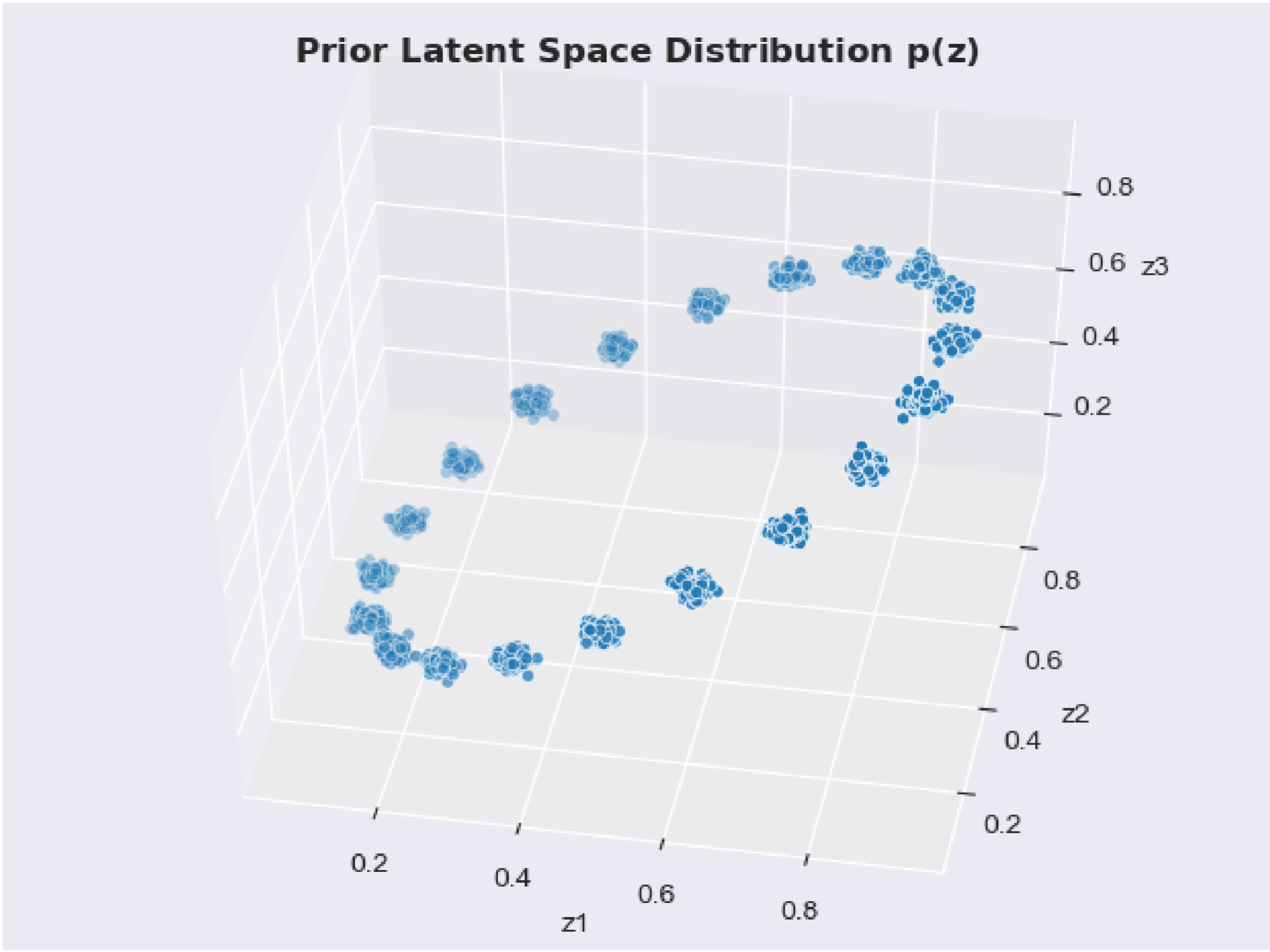
We propose an integration of adversarial autoencoders and machine learning methods to perform an objective classification among three transaction types, regular, local and global anomaly. The integration consists of using the autoencoder’s generated latent vectors as features for the supervised learning algorithms.
J. C. S. Silva, D. Macêdo, C. Zanchettin, A. L. I. Oliveira, A. T. Almeida-Filho
International Joint Conference on Neural Networks, 2021
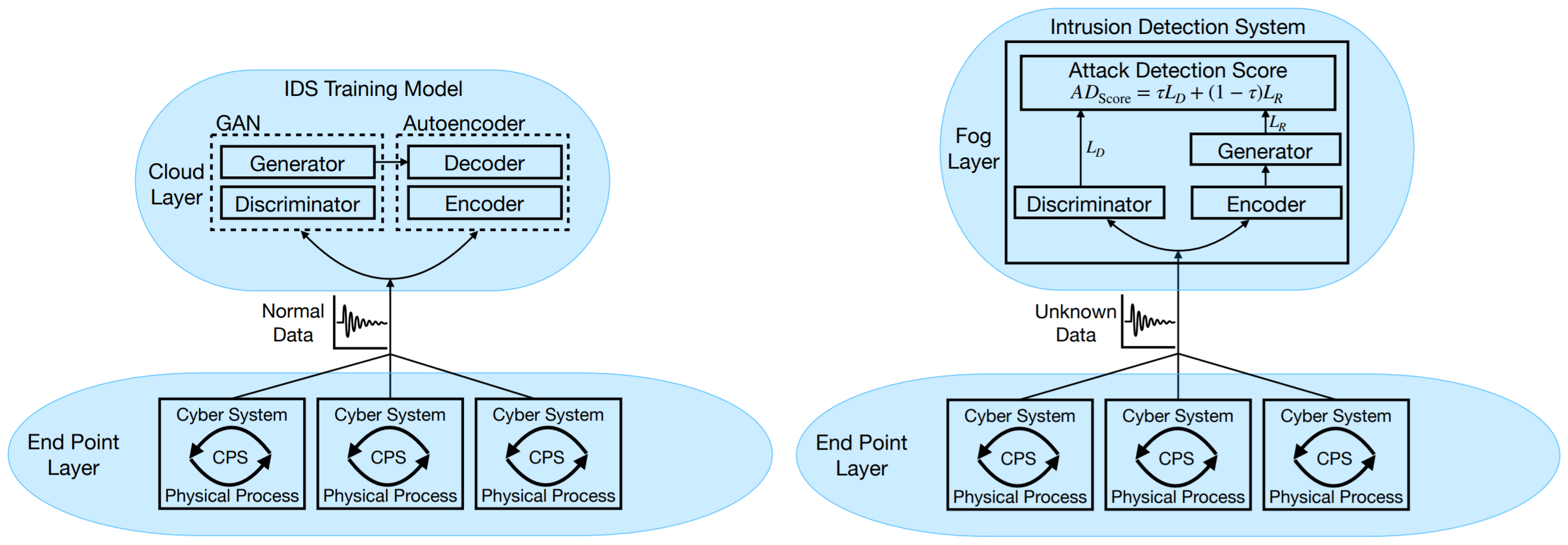
We propose FID-GAN, a novel fog-based, unsupervised intrusion detection system (IDS) for CPSs using GANs. The IDS is proposed for a fog architecture, which brings computation resources closer to the end nodes and thus contributes to meeting low-latency requirements.
P. F. de Araujo-Filho, G. Kaddoum, D. R. Campelo, A. G. Santos, D. Macêdo and C. Zanchettin
IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2020
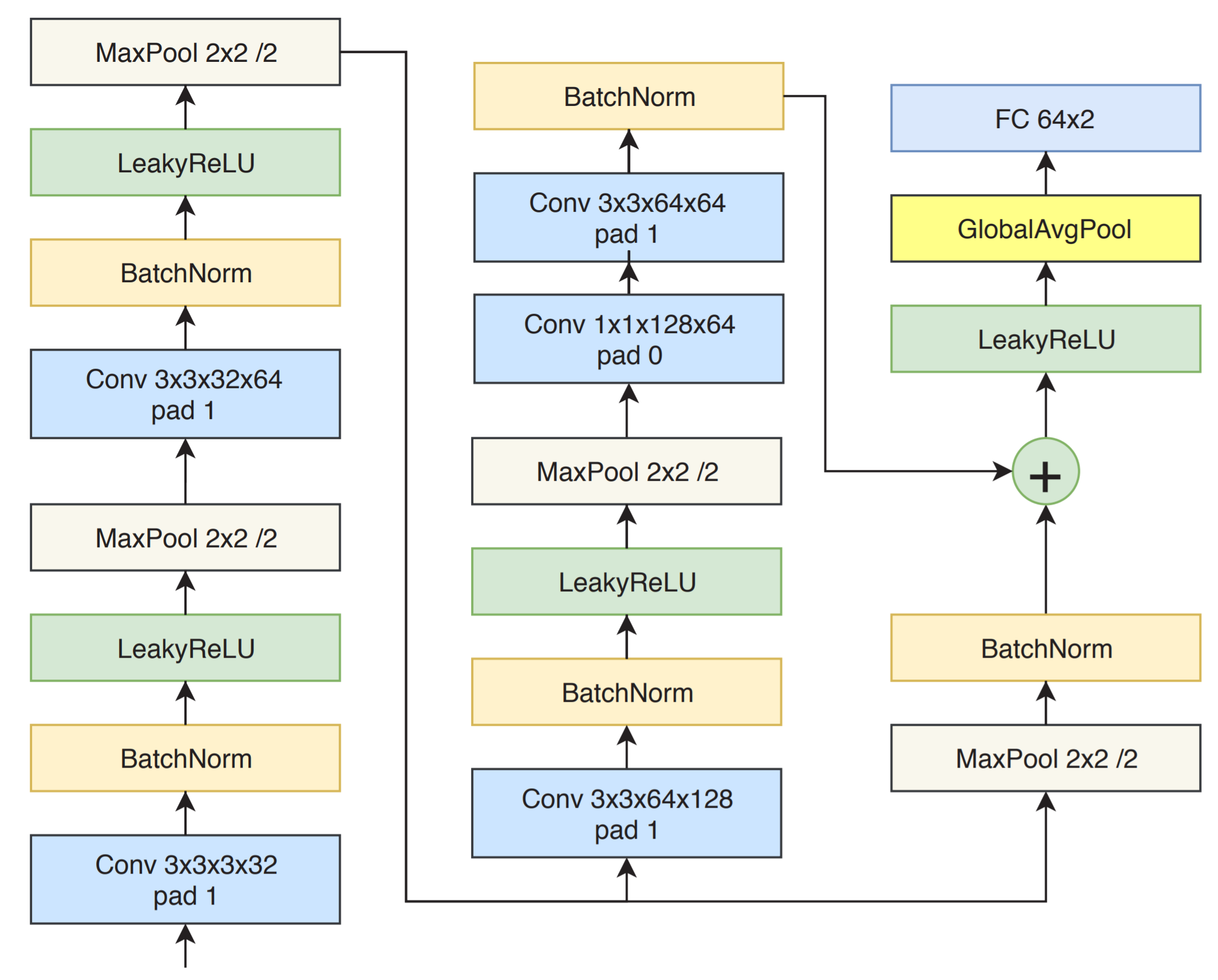
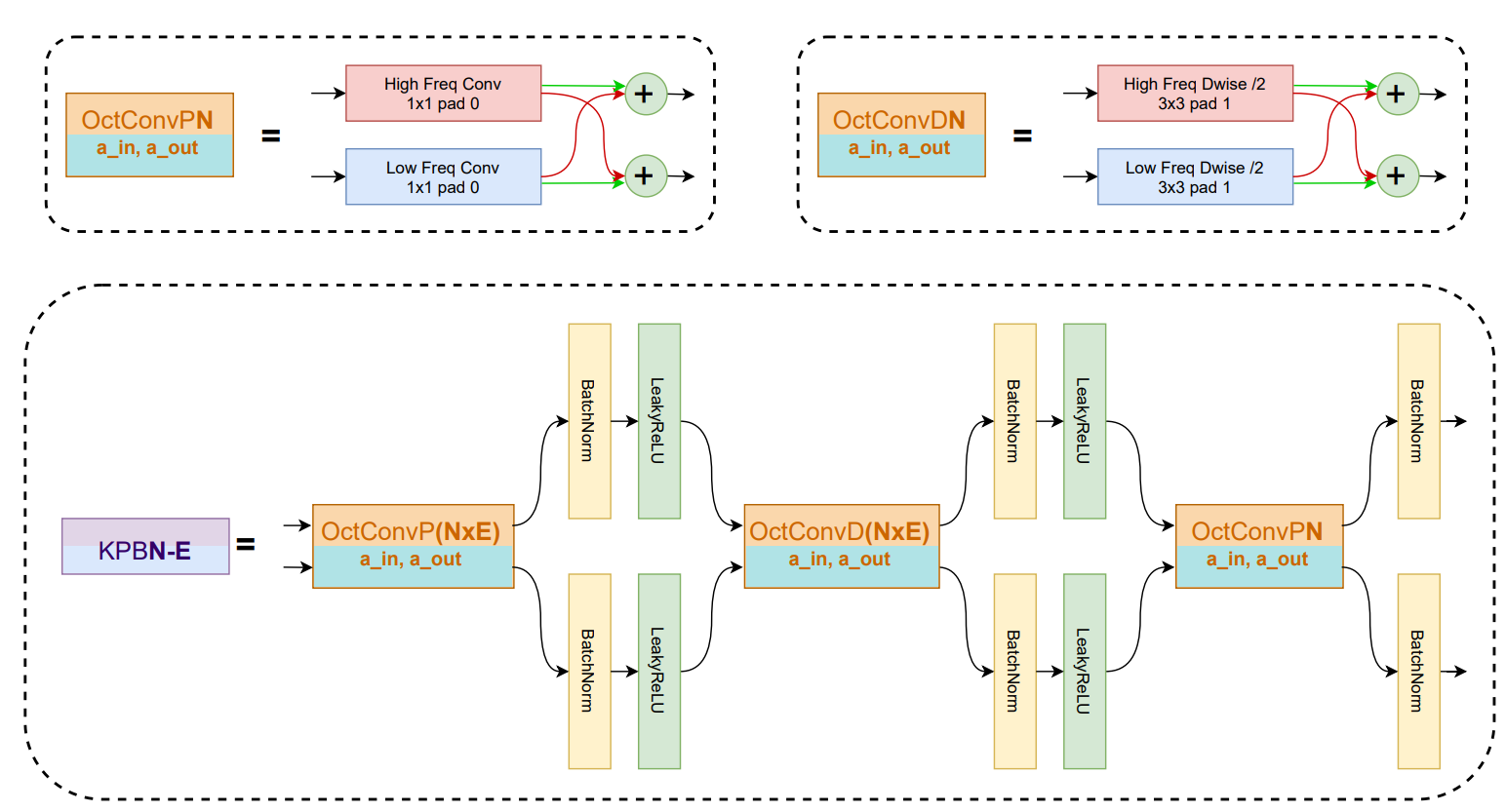
We propose a new deep learning architecture that requires fewer floating-point operations (flops) for fire recognition. Additionally, we propose a portable approach for fire recognition and the use of modern techniques such as inverted residual block, convolutions like depth-wise, and octave, to reduce the model’s computational cost.
A. Ayala, B. J. T. Fernandes, F. Cruz, D. Macêdo, A. L. I. Oliveira, C. Zanchettin
International Joint Conference on Neural Networks, 2020
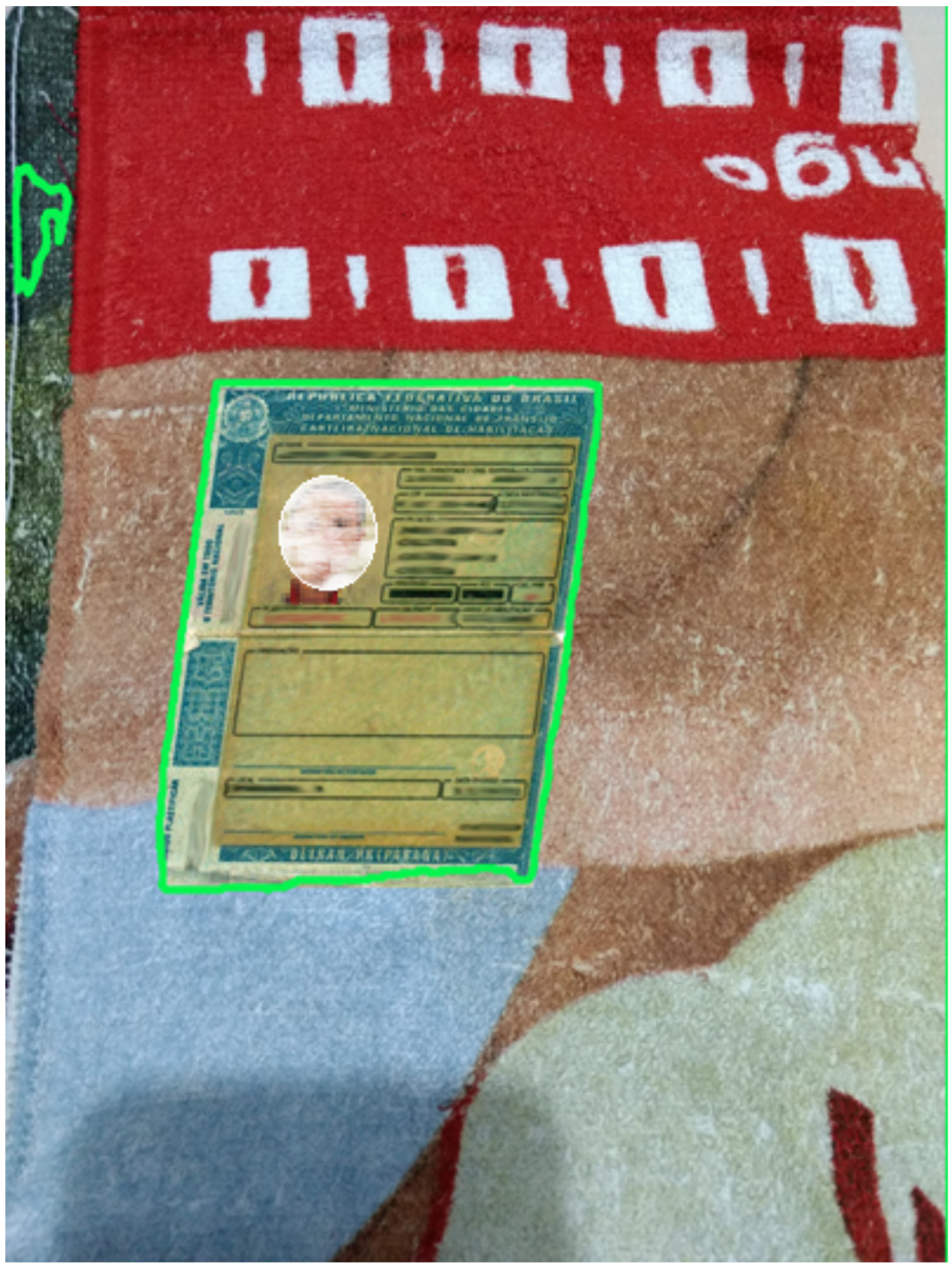

We investigated a method based on U-Net to detect the document edges and text regions in ID images. Besides the promising results on image segmentation, the U-Net based approach is computationally expensive for a real application, since the image segmentation is a customer device task. We propose a model optimization based on Octave Convolutions to qualify the method to situations where storage, processing, and time resources are limited, such as in mobile and robotic applications.
R. B. Neves Junior, L. F. Vercosa, D. Macêdo, A. L. I. Oliveira, C. Zanchettin
International Joint Conference on Neural Networks, 2020
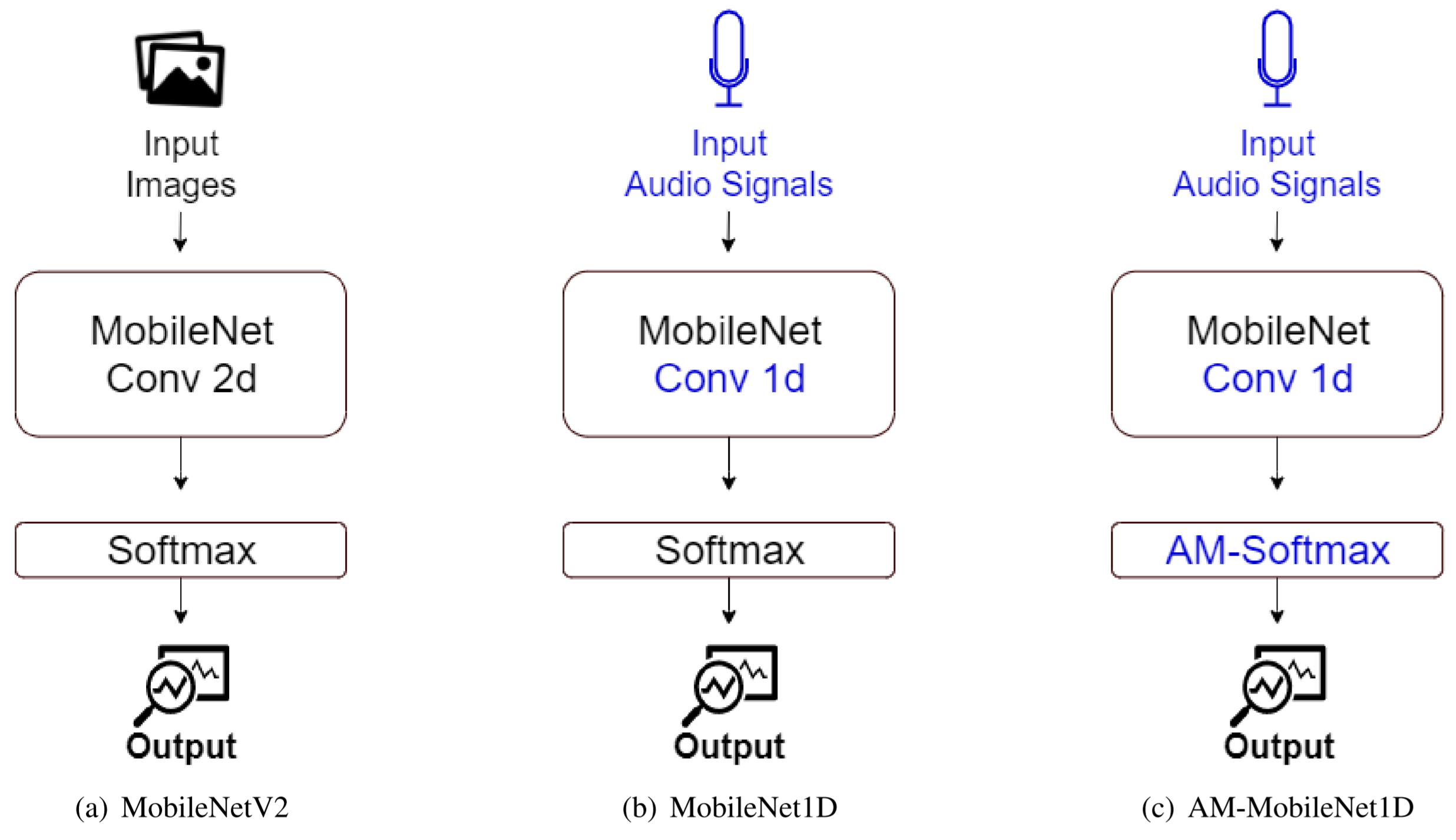
We propose a portable model called Additive Margin MobileNet1D (AM-MobileNet1D) to Speaker Identification on mobile devices. We evaluated the proposed approach on TIMIT and MIT datasets obtaining equivalent or better performances concerning the baseline methods. Additionally, the proposed model takes only 11.6 megabytes on disk storage against 91.2 from SincNet and AM-SincNet architectures, making the model seven times faster, with eight times fewer parameters.
J. A. C. Nunes, D. Macêdo, C. Zanchettin
International Joint Conference on Neural Networks, 2020
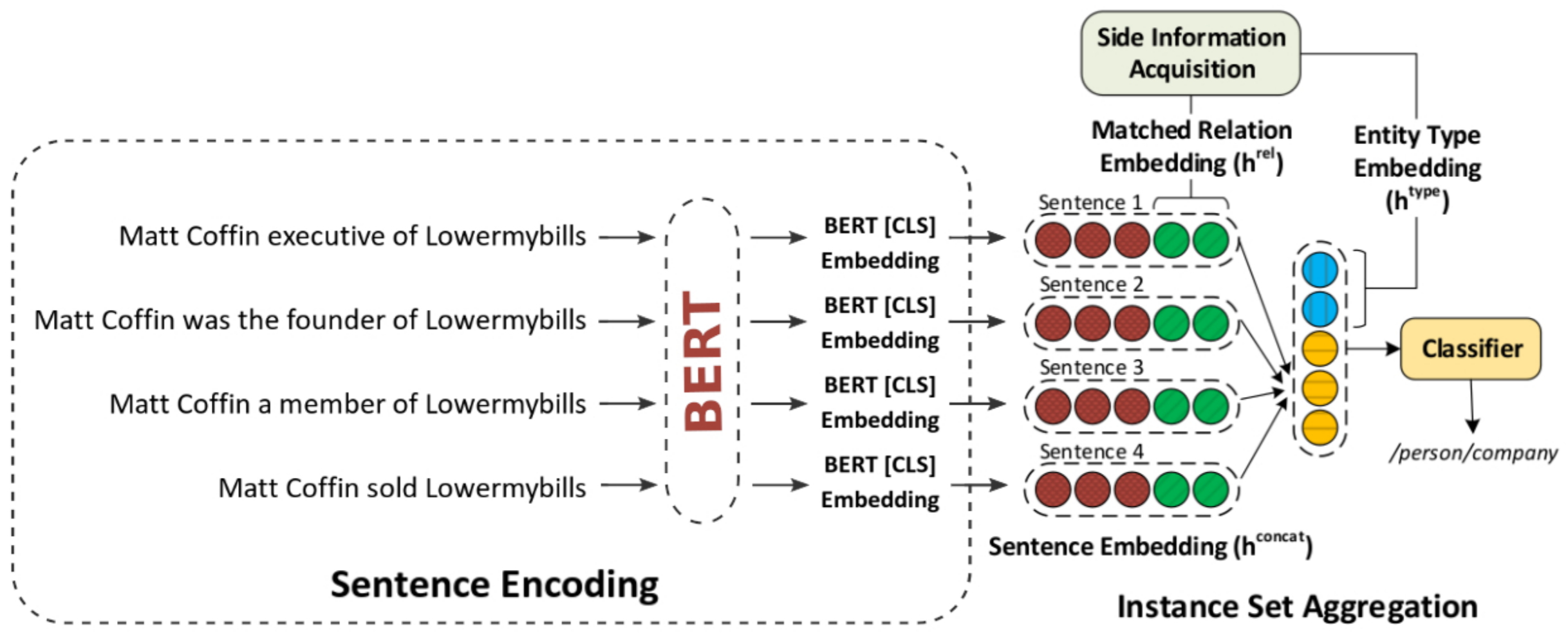
We propose a related approach to RESIDE also using additional side information, but simplifying the sentence encoding with BERT embeddings. Through experiments, we show the effectiveness of the proposed method in Google Distant Supervision and Riedel datasets concerning the BGWA and RESIDE baseline methods. Although Area Under the Curve is decreased because of unbalanced datasets, P@N results have shown that the use of BERT as sentence encoding allows superior performance to baseline methods.
J. Moreira, C. Oliveira, D. Macêdo, C. Zanchettin, L. A. Barbosa
International Joint Conference on Neural Networks, 2020
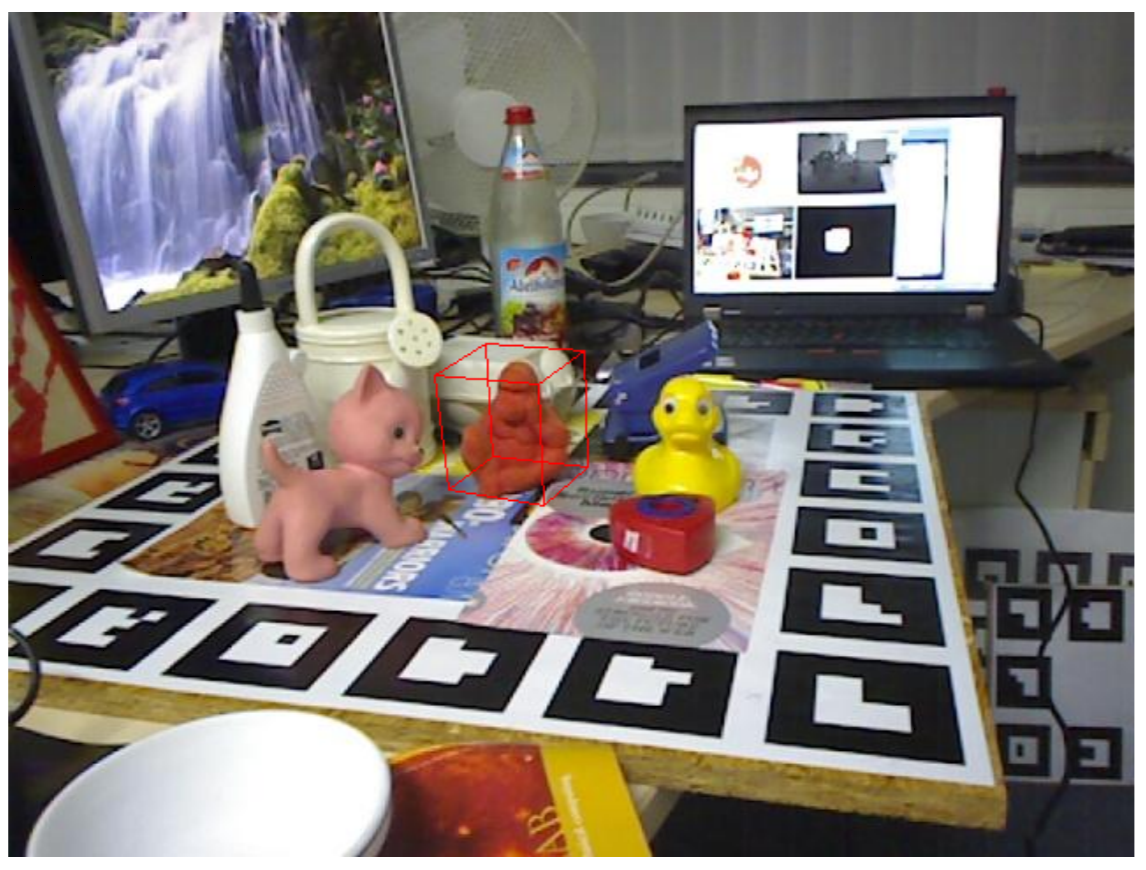

We propose an approach to reduce the complexity of 6DoF detection networks while maintaining accuracy. We used Knowledge Distillation to teach portables Convolutional Neural Networks (CNN) to learn from a real-time 6DoF detection CNN. The proposed method allows real-time applications using only RGB images while decreasing the hardware requirements. We used the LINEMOD dataset to evaluate the proposed method, and the experimental results show that the proposed method reduces the memory requirement by almost 99\% in comparison to the original architecture with the cost of reducing half the accuracy in one of the metrics.
H. Felix, W. Rodrigues, D. Macêdo, F. Simões, A. L. I. Oliveira; V. Teichrieb, C. Zanchettin
International Joint Conference on Neural Networks, 2020
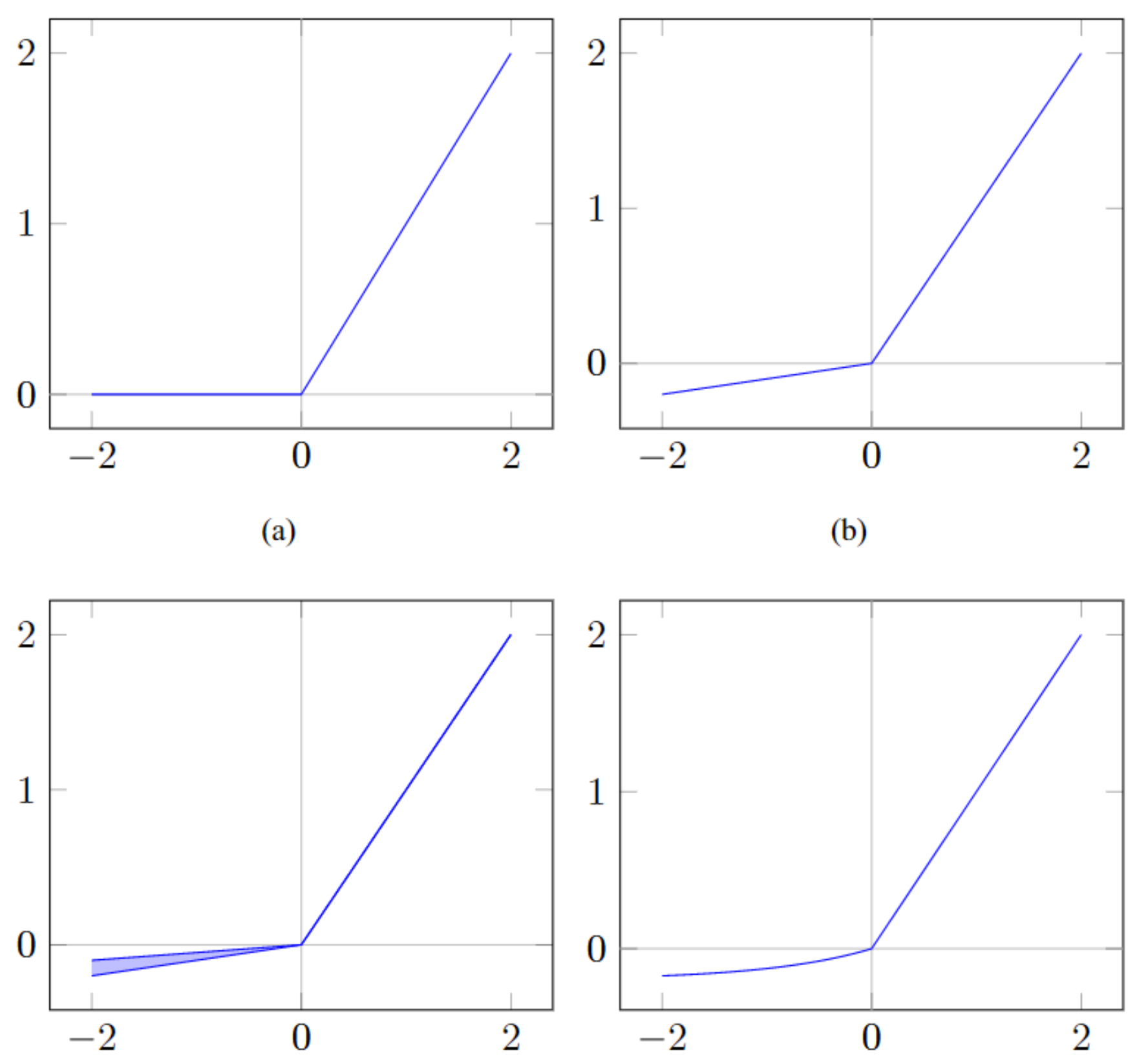
We propose the activation function Displaced Rectifier Linear Unit (DReLU) by conjecturing that extending the identity function of ReLU to the third quadrant enhances compatibility with batch normalization. Moreover, we used statistical tests to compare the impact of using distinct activation functions (ReLU, LReLU, PReLU, ELU, and DReLU) on the learning speed and test accuracy performance of standardized VGG and Residual Networks state-of-the-art models.
D. Macêdo, C. Zanchettin, A. L.I. Oliveira, T. B. Ludermir
Expert Systems with Applications, 2019
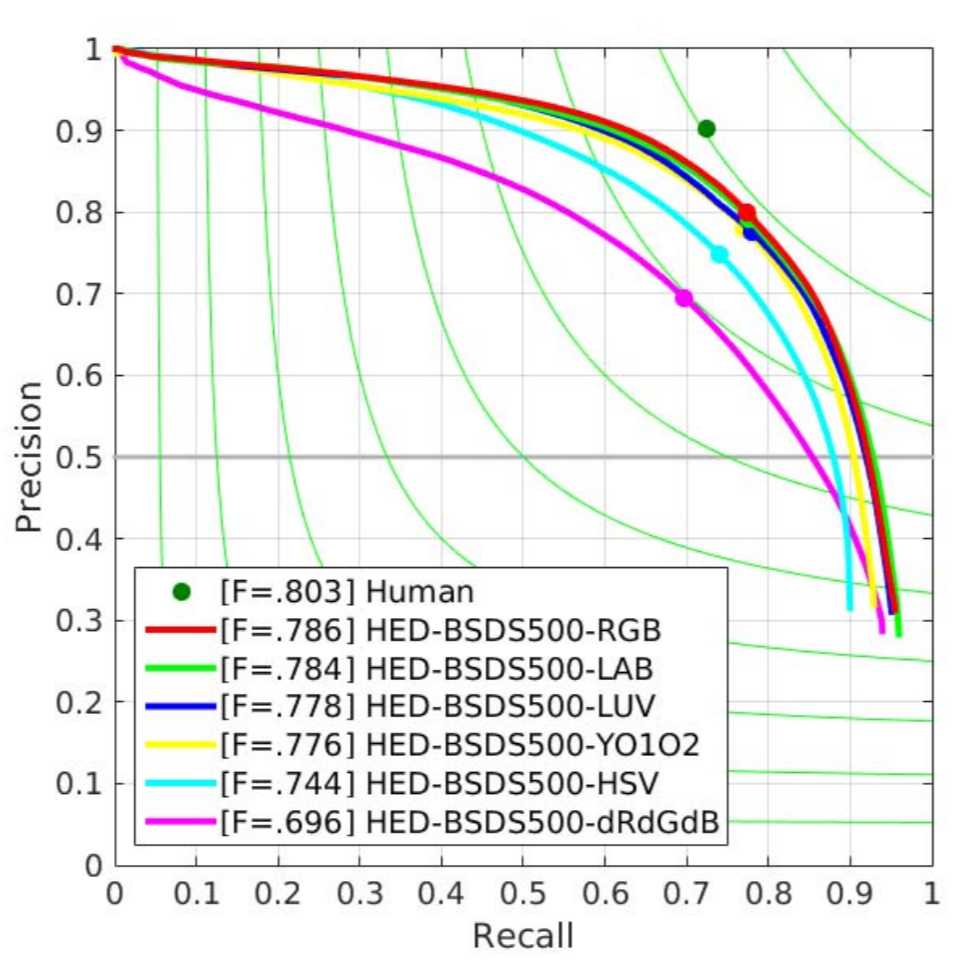
We provide a qualitative analysis of boundary detection algorithms based on CNN but considering images in different color models. We have used the color models RGB, Lab, Luv, dRdGdB, YO1O2 and HSV for this analysis. The Holistically-Nested Edge Detection (HED) and Convolutional Encoder Decoder Network (CEDN) are the CNN’s chosen due to their high performance.
T. J. Dos Santos, C. A. B. Mello, C. Zanchettin, T. V. M. De Souza
International Joint Conference on Neural Networks, 2019
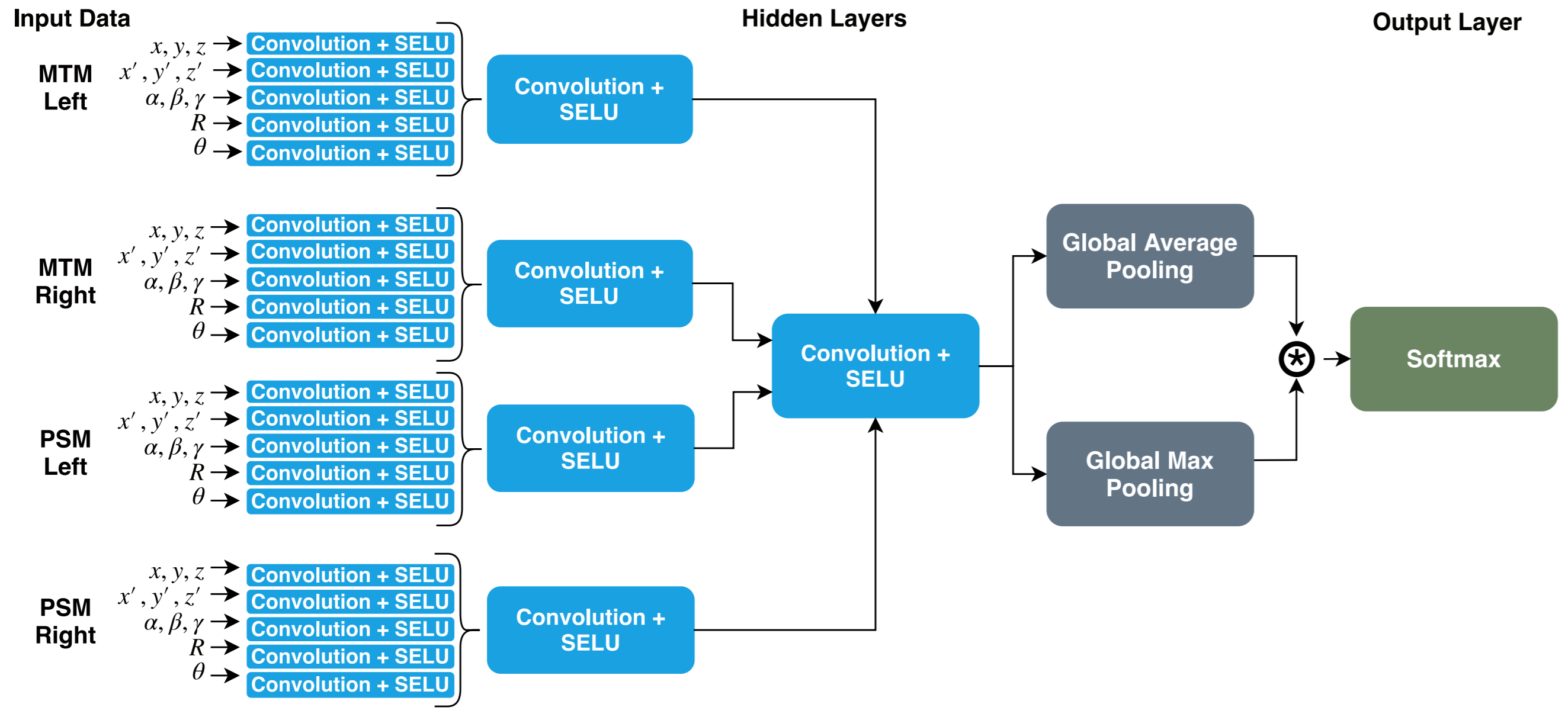
We propose a novel CNN architecture for automated robot-assisted skill assessment. We explore the use of the SELU activation function and a global mixed pooling approach based on the average and max-pooling layers. Finally, we examine two types of convolutional layers, real-value and quaternion-valued. The results suggest that our model presents a higher average accuracy across the three surgical subtasks of the JIGSAWS dataset.
D. Castro, D. Pereira, C. Zanchettin, D. Macêdo, B. L. D. Bezerra
International Joint Conference on Neural Networks, 2019
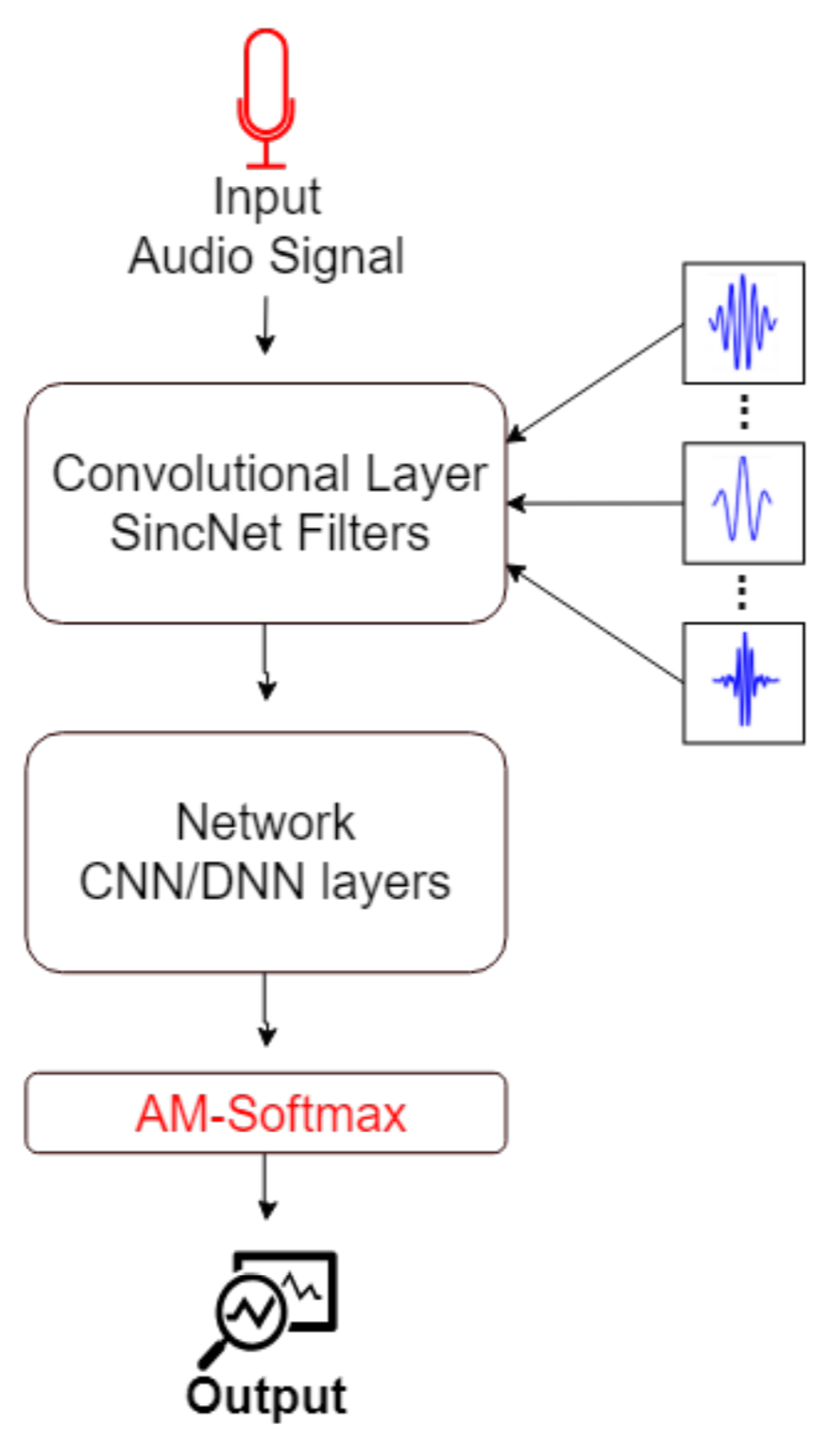
The Softmax loss function is a widely used function in deep learning methods, but it is not the best choice for all kind of problems. For distance-based problems, one new Softmax based loss function called Additive Margin Softmax (AM-Softmax) is proving to be a better choice than the traditional Softmax. The AM-Softmax introduces a margin of separation between the classes that forces the samples from the same class to be closer to each other and also maximizes the distance between classes. In this paper, we propose a new approach for speaker recognition systems called AM-SincNet, which is based on the SincNet but uses an improved AM-Softmax layer.
J. A. C. Nunes, D. Macêdo, C. Zanchettin
International Joint Conference on Neural Networks, 2019
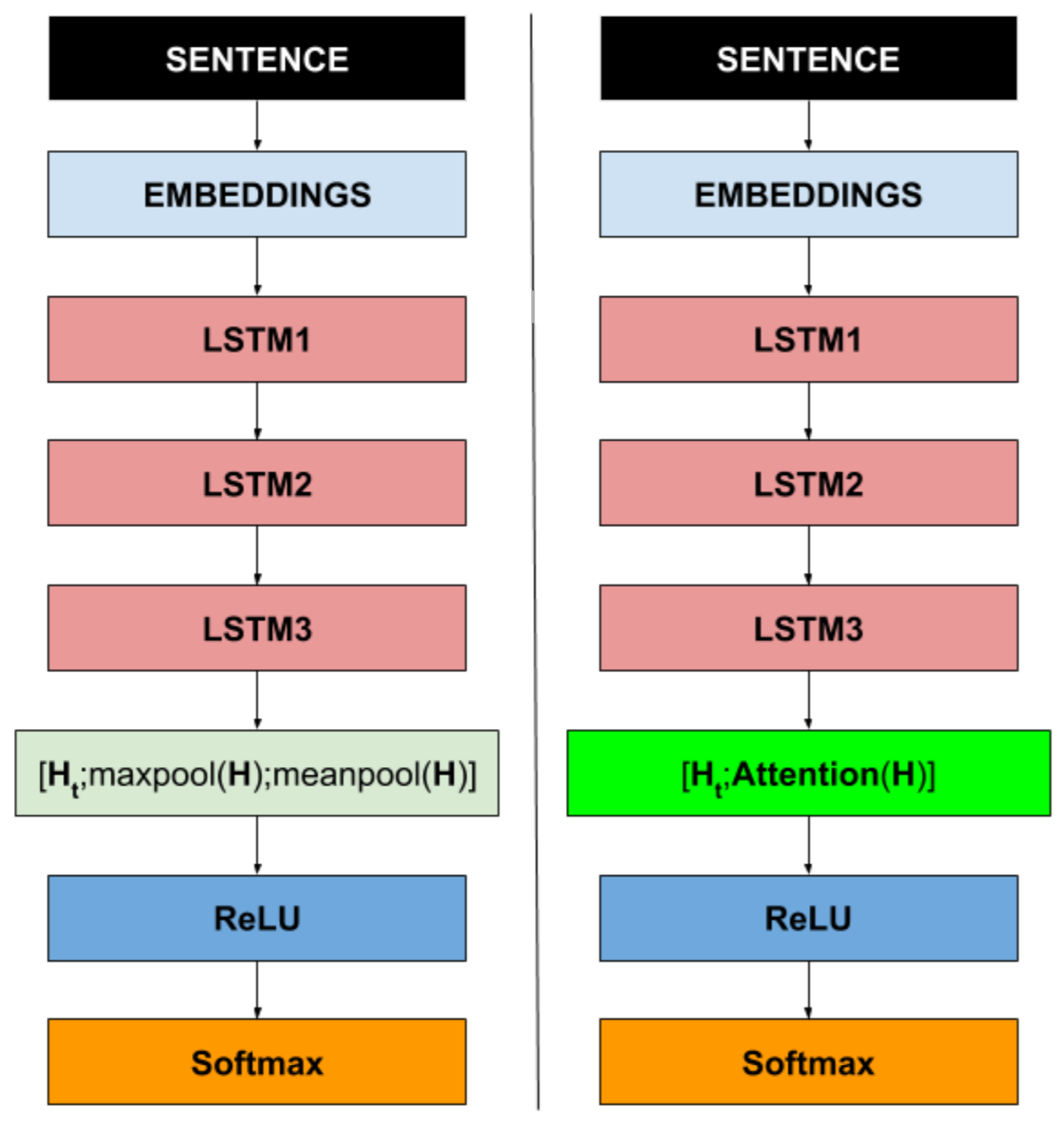
The Universal Language Model Fine-Tuning (ULMFiT) is a recent approach which proposes to train a language model and transfer its knowledge to a final classifier. During the classification step, ULMFiT uses a max and average pooling layer to select the useful information of an embedding sequence. We propose to replace max and average pooling layers with a soft attention mechanism. The goal is to learn the most important information of the embedding sequence rather than assuming that they are max and average values.
F. A. O. SANTOS, K. L. Ponce-Guevara, D. Macêdo, C. Zanchettin
International Joint Conference on Neural Networks, 2019
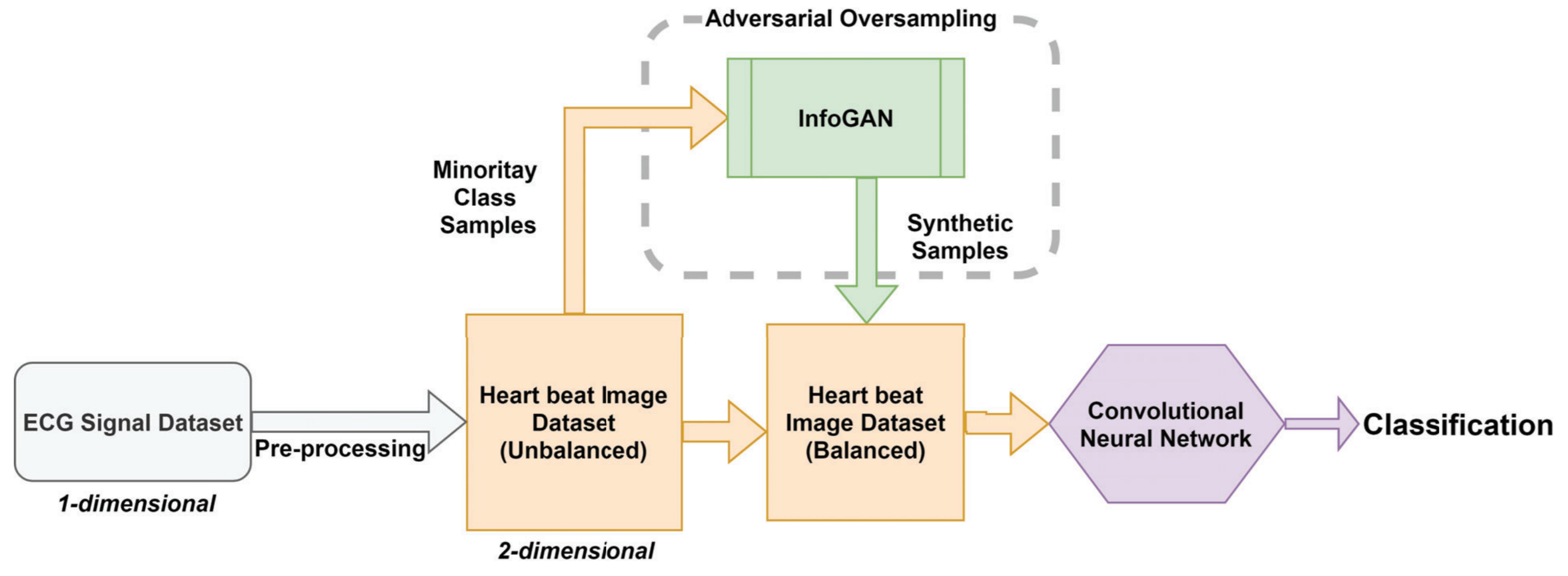
We propose a two-dimensional Convolutional Neural Network for classification after using a InfoGAN architecture for generating synthetic images to unbalanced classes. We call this proposal Adversarial Oversampling and compare it with the classical oversampling methods as SMOTE, ADASYN, and Random Oversampling. The results show that the proposed approach improves the classifier performance for the minority classes without harming the performance in the balanced classes.
J. L. P. LIMA, D. Macêdo, C. Zanchettin
International Joint Conference on Neural Networks, 2019
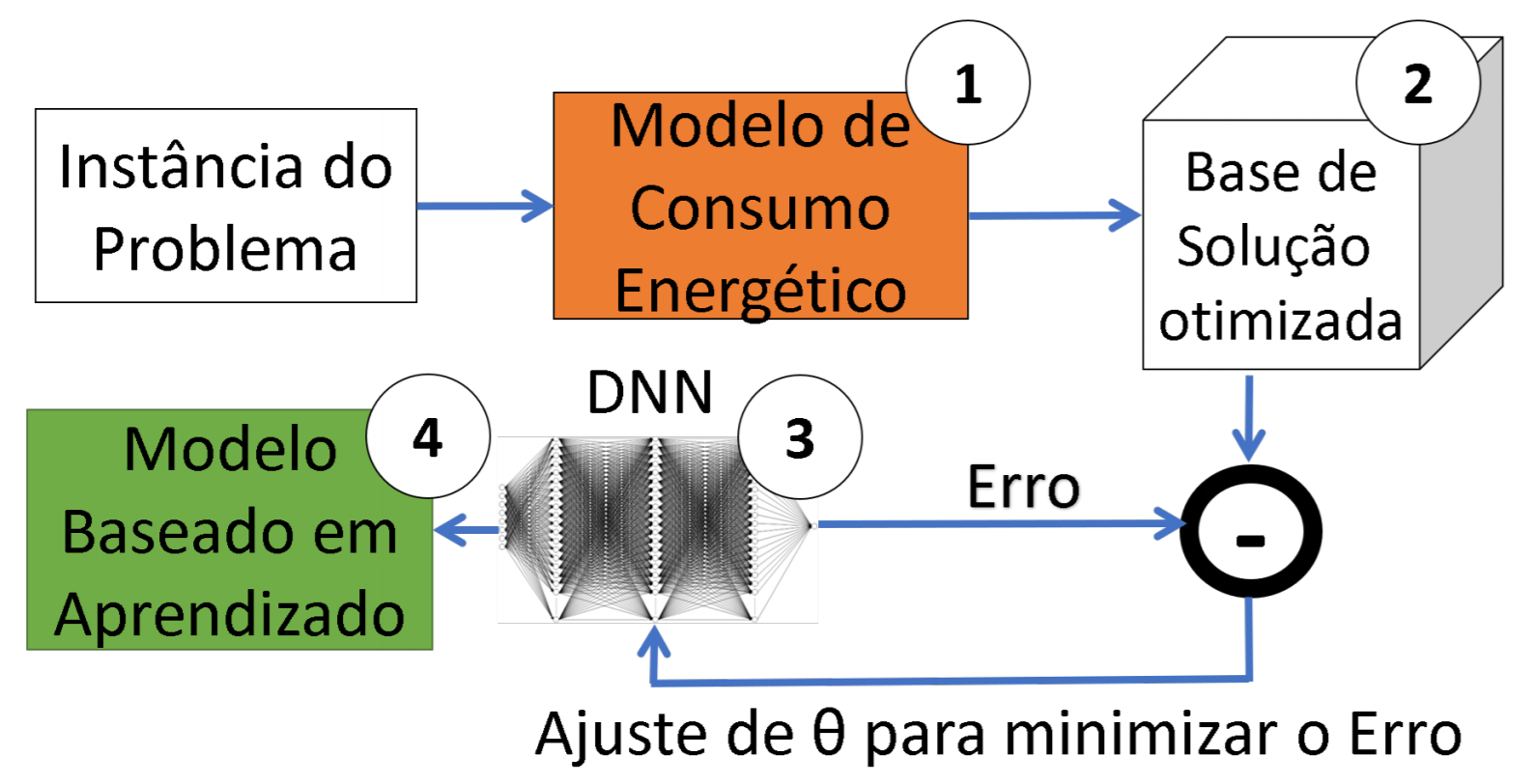
O presente artigo propõe uma nova abordagem baseada em aprendizagem de máquina que considera a entrada e a saı́da de um algoritmo de controle de consumo de energia em redes ad hoc slotted Aloha de múltiplas varáveis. Resultados mostram que a rede neural proposta obteve melhor desempenho em relação ao tempo de processamento e custo computacional quando comparado aos algoritmos de controle energético de busca gulosa utilizados atualmente.
P. F. C. Barbosa, D. Macêdo, B. A. Da Silva, R. M. De Moraes, C. Zanchettin
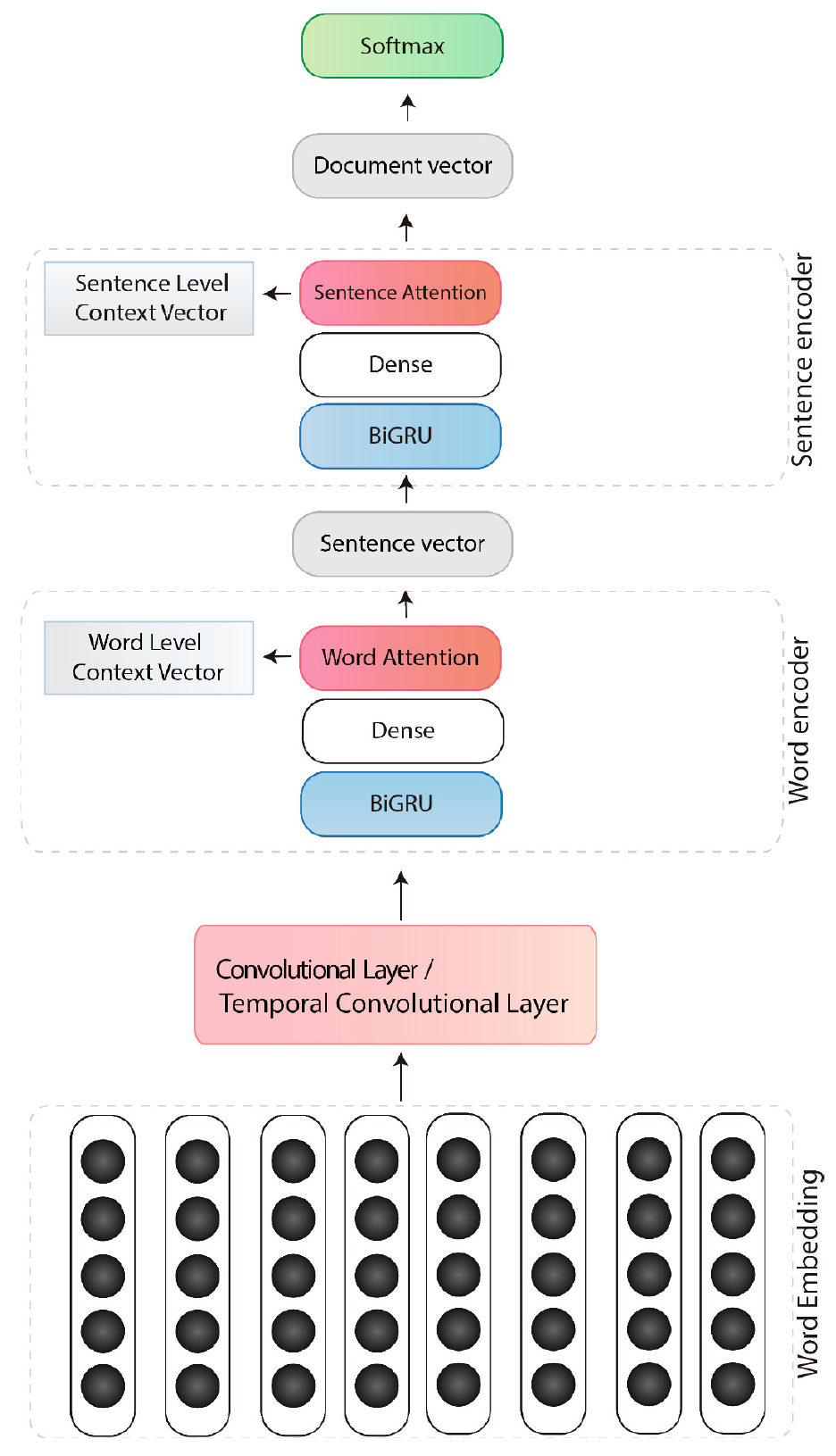
We propose a new approach based on a combination of convolutional neural networks, gated recurrent units, and attention mechanisms for document classification tasks. We use of convolution layers varying window sizes to extract more meaningful, generalizable and abstract features by the hierarchical representation.
J. Abreu, L. Fred, D. Macêdo, C. Zanchettin
International Conference on Artificial Neural Networks, 2019
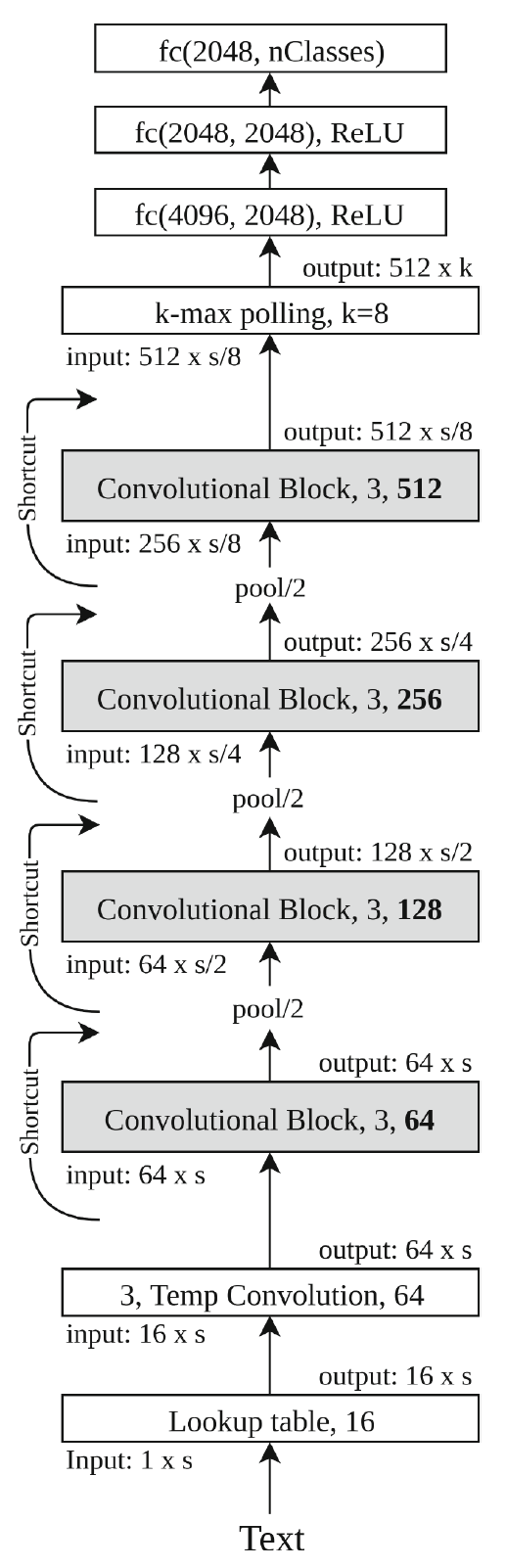
We propose to modify the structure of the Very Deep Convolutional Neural Networks (VDCNN) model to reduce its storage size while keeping the model performance. In this paper, we evaluate the impact of Temporal Depthwise Separable Convolutions and Global Average Pooling in the network parameters, storage size, dedicated hardware dependence, and accuracy. The proposed squeezed model (SVDCNN) is between 10x and 20x smaller than the original version, depending on the network depth, maintaining a maximum disk size of 6MB.
A. B. Duque, L. L. Santos, D. Macêdo, C. Zanchettin
International Conference on Artificial Neural Networks, 2019
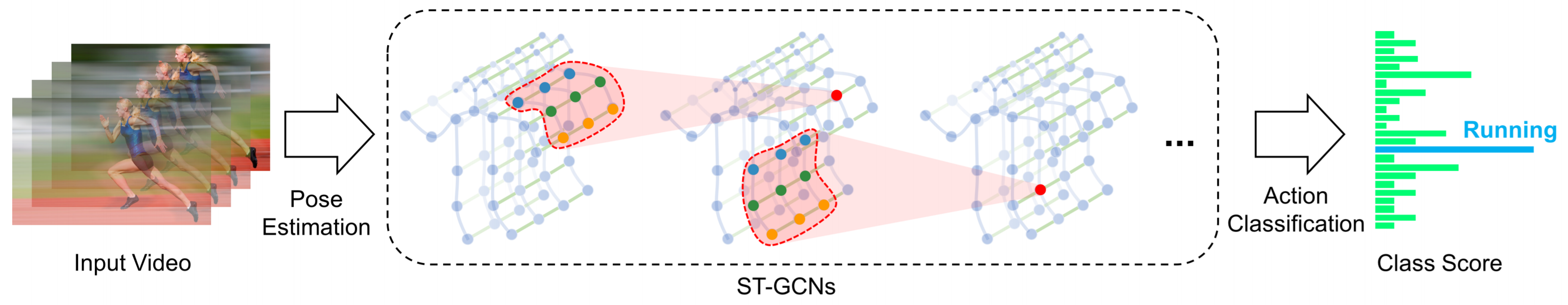
We propose a new approach of Spatial-Temporal Graph Convolutional Network to sign language recognition based on the human skeletal movements. The method uses graphs to capture the signs dynamics in two dimensions, spatial and temporal, considering the complex aspects of the language. Additionally, we present a new dataset of human skeletons for sign language based on ASLLVD to contribute to future related studies.
C. C. de Amorim, D. Macêdo, C. Zanchettin
International Conference on Artificial Neural Networks, 2019
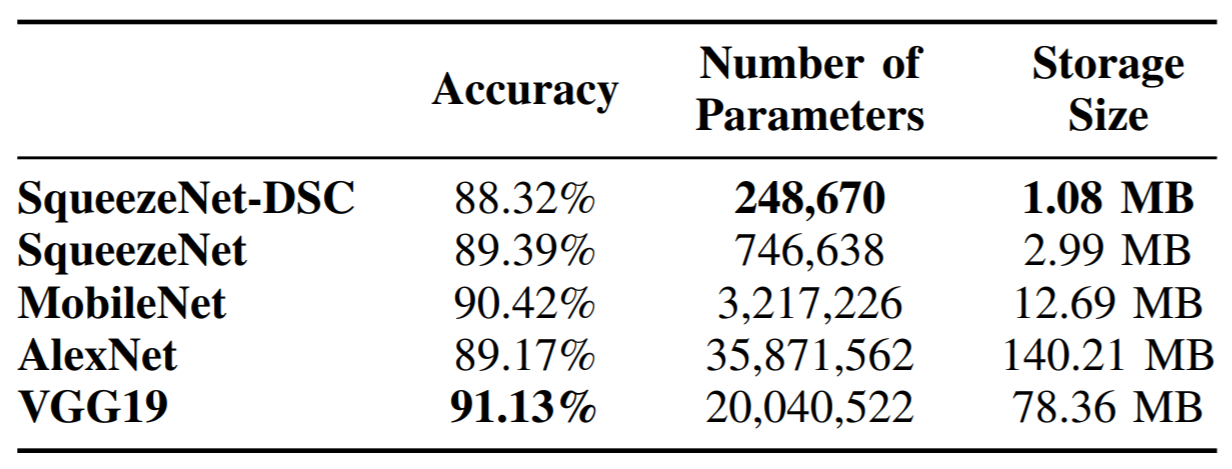
We investigate the effects of storage space reduction in SqueezeNet as it relates to inference time when processing single test samples. In order to reduce the storage space, we suggest adjusting SqueezeNet’s Fire Modules to include Depthwise Separable Convolutions (DSC). The resulting network, referred to as SqueezeNet-DSC, is compared to different convolutional neural networks such as MobileNet, AlexNet, VGG19, and the original SqueezeNet itself.
A. G. Santos, C. O. De Souza, C. Zanchettin, D. Macêdo, A. L. I Oliveira, T. B. Ludermir
International Joint Conference on Neural Networks, 2018
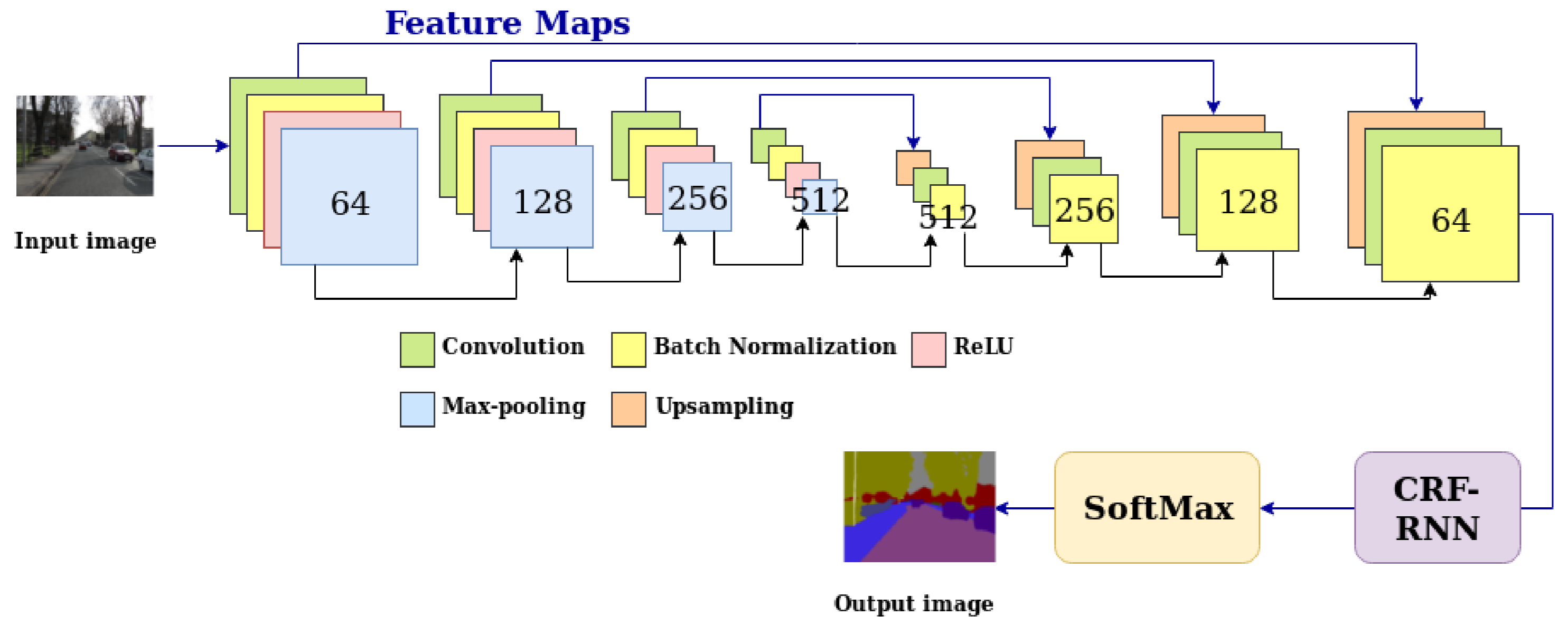
We propose some modifications in the SegNet-Basic architecture by using a post-processing segmentation layer (using Conditional Random Fields) and by transferring high resolution features combined to the decoder network. The proposed method was evaluated in the dataset CamVid. Moreover, it was compared with important variants of SegNet and showed to be able to improve the overall accuracy of SegNet-Basic by up to 17.5%.
L. A. De Oliveira Junior; H. R. Medeiros, D. Macêdo, C. Zanchettin, A. L. I. Oliveira, T. B. Ludermir
International Joint Conference on Neural Networks, 2018
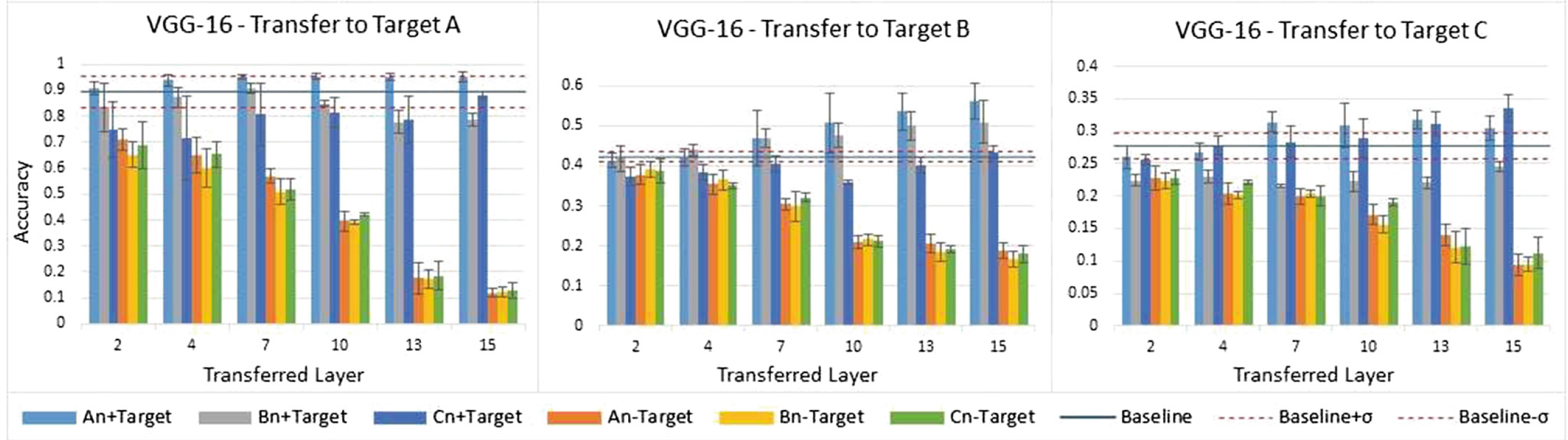
We performed a statistical analysis through several experiments in which the convolutional neural networks (LeNet-5, AlexNet, VGG-11 and VGG-16) were trained and transferred to different target tasks layer by layer. We show that when working with complex low-quality images and small datasets, fine-tuning the transferred features learned from a low complexity source dataset gives the best results.
M. D. S. Wanderley, L. A. Bueno, C. Zanchettin, A. L. I. Oliveira
International Conference on Neural Networks, 2017